Understanding The Power Consumption Of Household Appliances: A Guide To Energy Efficiency
Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Related Articles: Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Energy Efficiency
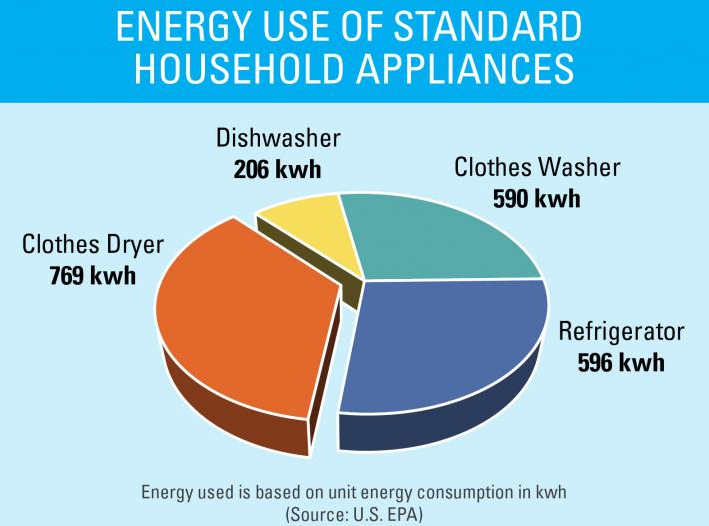
Household appliances are an integral part of modern life, providing convenience and comfort. However, their operation comes at a cost – energy consumption. Understanding how much energy each appliance uses is crucial for making informed decisions about energy efficiency, reducing utility bills, and minimizing environmental impact. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the power consumption of common household items, highlighting the importance of energy awareness and offering practical tips for reducing energy usage.
Power Consumption: The Basics
Power consumption is measured in watts (W), with higher wattage indicating greater energy use. Appliances typically display their wattage on their nameplate or in their user manuals. It’s important to note that wattage is a measure of instantaneous power consumption, while energy consumption is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) – the amount of energy used over a specific period of time.
Common Household Appliances and Their Power Consumption
1. Lighting:
- Incandescent Bulbs: These traditional bulbs are notorious for being energy inefficient. A standard 60-watt incandescent bulb consumes 60 watts of power when turned on.
- LED Bulbs: LED bulbs are significantly more energy-efficient, using only 10-15 watts to produce the same amount of light as a 60-watt incandescent bulb.
- Fluorescent Bulbs: These bulbs offer a good balance between efficiency and cost, consuming around 15-20 watts for similar light output.
2. Kitchen Appliances:
- Refrigerator: A typical refrigerator consumes around 150-200 watts when running, although newer models with energy-efficient features can consume significantly less.
- Oven: Electric ovens can consume anywhere from 2,000 to 4,000 watts, while gas ovens typically consume less.
- Microwave: Microwaves consume around 1,000 watts when in use, but their energy consumption is generally lower than ovens.
- Dishwasher: Dishwashers consume approximately 1,200 to 1,800 watts during a cycle.
- Coffee Maker: Coffee makers consume around 1,000 watts while brewing.
3. Laundry Appliances:
- Washing Machine: Washing machines consume around 500 to 1,500 watts depending on the load size and water temperature.
- Clothes Dryer: Electric dryers consume significantly more power than washing machines, typically ranging from 3,000 to 5,000 watts. Gas dryers consume less energy but require a gas line.
4. Electronics:
- Television: Modern televisions consume around 100 to 200 watts, but older models can consume significantly more.
- Computer: Desktop computers can consume around 200 to 400 watts, while laptops consume less, typically around 50 to 100 watts.
- Gaming Console: Gaming consoles consume around 100 to 200 watts while in use.
5. Heating and Cooling:
- Air Conditioner: Air conditioners can consume significant amounts of energy, typically ranging from 1,000 to 5,000 watts depending on the size and efficiency.
- Heater: Electric heaters consume around 1,500 to 2,500 watts, while gas heaters typically consume less.
The Importance of Energy Awareness
Understanding the power consumption of household appliances is crucial for several reasons:
- Reducing Energy Bills: By using energy-efficient appliances and reducing unnecessary energy consumption, individuals can significantly lower their utility bills.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption helps to minimize greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
- Extending Appliance Lifespan: Using appliances properly and avoiding overloading them can help extend their lifespan and reduce the need for premature replacements.
Tips for Reducing Energy Consumption
- Choose Energy-Efficient Appliances: Look for appliances with Energy Star ratings, which indicate high energy efficiency.
- Unplug Unused Appliances: Unplug appliances that are not in use, as they can still consume energy in standby mode.
- Use Appliances Efficiently: Optimize appliance settings for efficient operation, such as using cold water for laundry or choosing the appropriate cooking time for ovens.
- Replace Incandescent Bulbs with LEDs: LED bulbs offer significantly improved energy efficiency, reducing lighting costs and energy consumption.
- Consider Renewable Energy Sources: Investigate the possibility of installing solar panels or wind turbines to generate renewable energy for your home.
FAQs
Q: How do I calculate the energy consumption of an appliance?
A: To calculate the energy consumption of an appliance, multiply its wattage by the number of hours it is used per day, then divide by 1,000 to convert to kilowatt-hours (kWh). For example, a 100-watt light bulb used for 5 hours per day consumes 0.5 kWh (100 watts x 5 hours / 1,000).
Q: What is the average energy consumption of a household?
A: The average household energy consumption varies depending on factors such as location, climate, and household size. However, a typical household in the United States consumes around 10,000 kWh per year.
Q: How can I monitor my energy consumption?
A: Many utility companies offer online tools or smart meters that allow you to track your energy consumption in real-time. You can also purchase energy monitors that plug into your electrical outlets to measure the energy consumption of specific appliances.
Conclusion
Understanding the power consumption of household appliances is essential for making informed decisions about energy efficiency, reducing utility bills, and contributing to a sustainable future. By choosing energy-efficient appliances, using them effectively, and adopting energy-saving habits, individuals can significantly reduce their energy footprint and contribute to a more sustainable world.


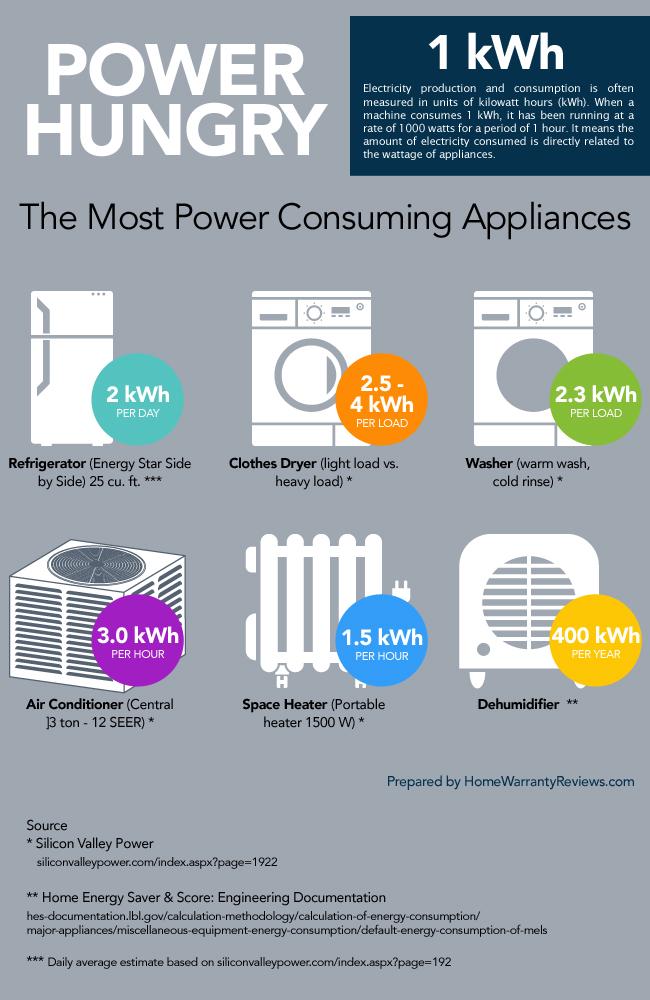

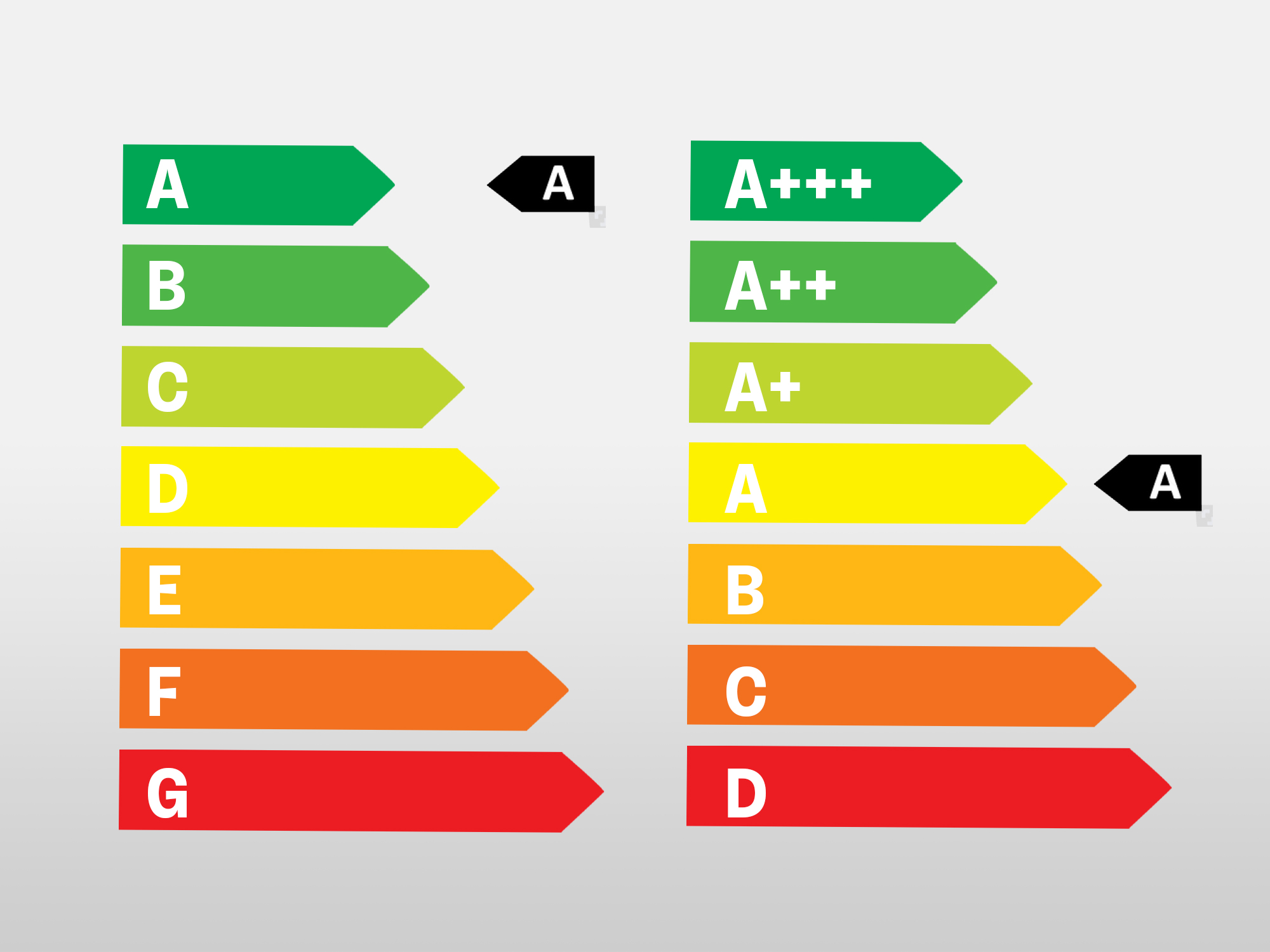


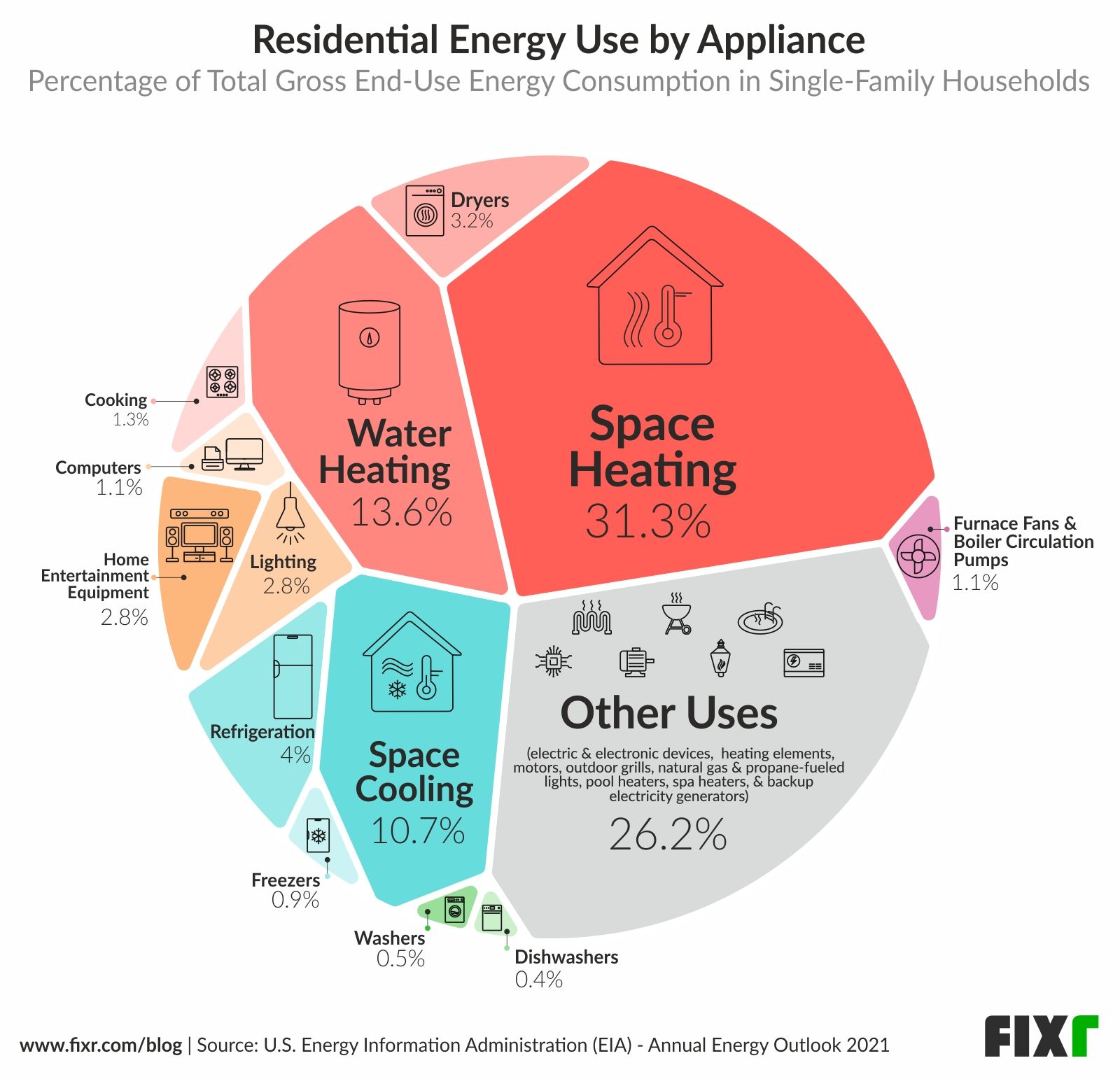
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Power Consumption of Household Appliances: A Guide to Energy Efficiency. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply