Understanding The Energy Footprint Of Our Homes: A Comprehensive Guide To Household Energy Consumption
Understanding the Energy Footprint of Our Homes: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Energy Consumption
Related Articles: Understanding the Energy Footprint of Our Homes: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Energy Consumption
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to Understanding the Energy Footprint of Our Homes: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Energy Consumption. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding the Energy Footprint of Our Homes: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Energy Consumption

Our homes are often seen as havens of comfort and convenience, but they also represent a significant portion of our overall energy consumption. Understanding how much energy various household items utilize is crucial for making informed decisions about energy efficiency, reducing our environmental impact, and saving money on utility bills.
This article delves into the energy consumption of common household appliances and devices, providing a detailed breakdown of their energy usage and offering practical tips for minimizing energy waste.
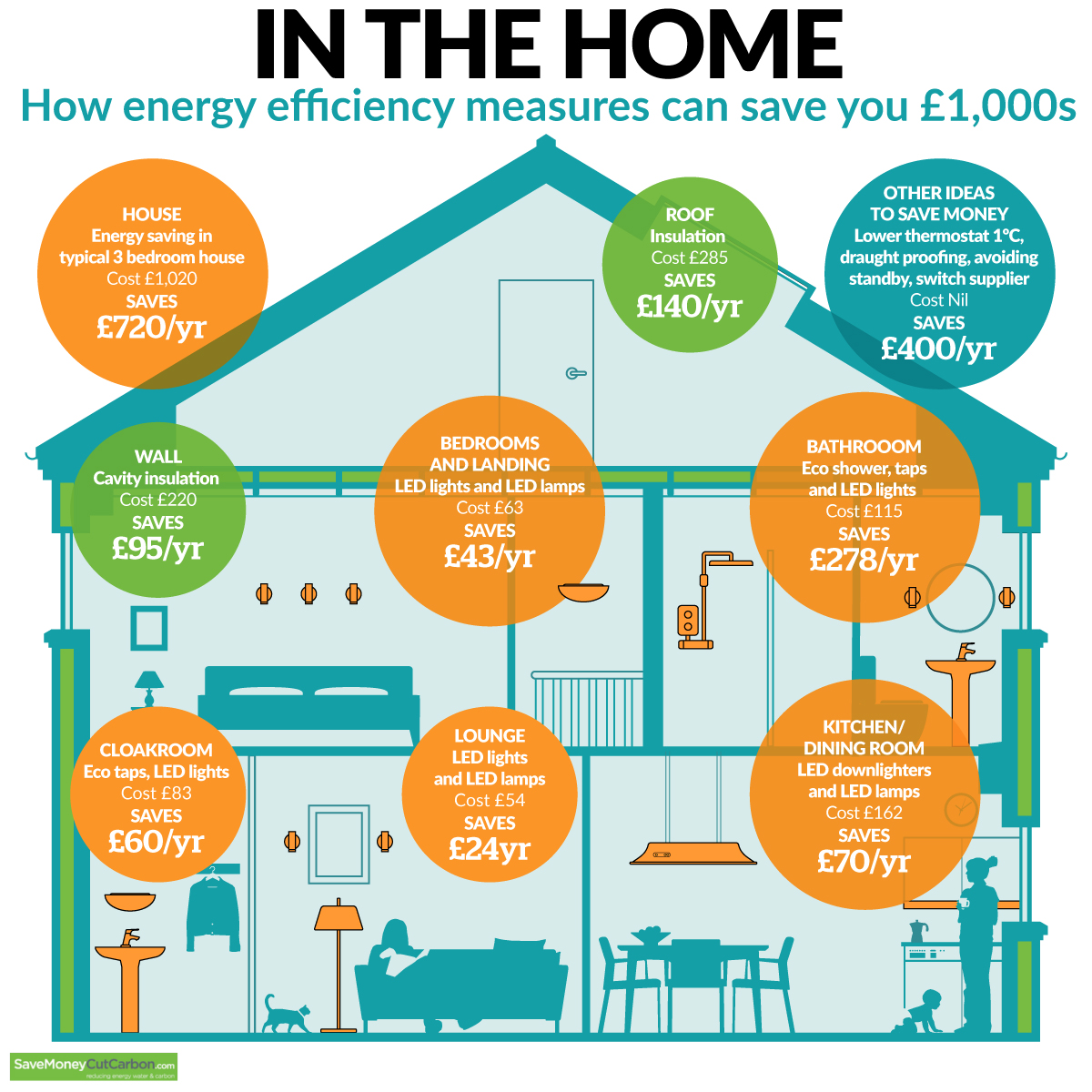
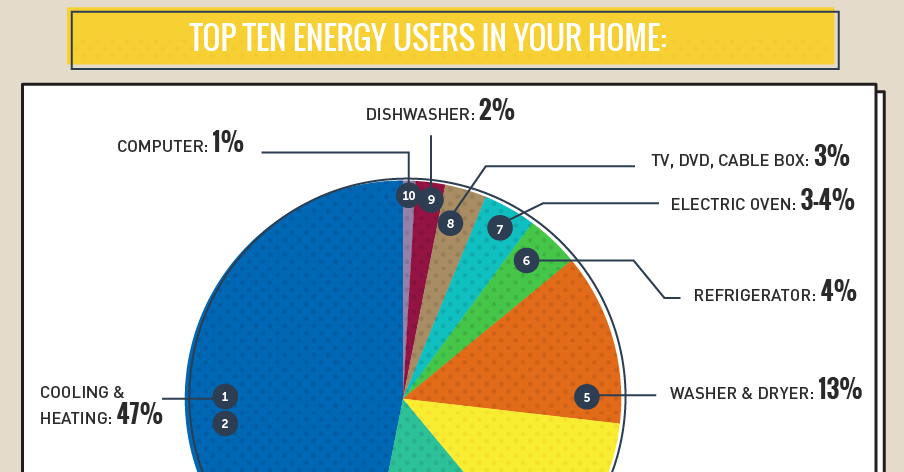
The Energy Hogs: Appliances with Significant Energy Consumption
1. Heating and Cooling Systems:
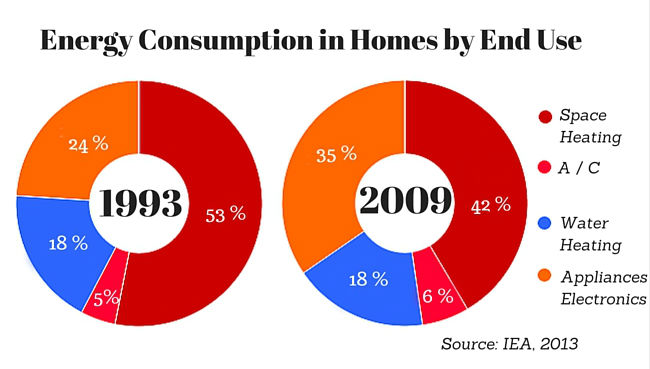
- Heating: Heating systems, whether fueled by natural gas, oil, electricity, or propane, account for a substantial portion of household energy consumption, often exceeding 40% in colder climates.
- Cooling: Air conditioning, particularly in warmer regions, can contribute significantly to energy bills, especially during peak summer months. Energy-efficient models with higher SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) ratings can significantly reduce energy consumption.
2. Water Heating:
- Water Heaters: Water heaters, typically gas or electric, are responsible for heating water for showers, baths, dishwashing, and laundry. Tankless water heaters offer greater efficiency compared to traditional tank-style heaters.
- Dishwashers: Dishwashers consume energy for heating water and running the wash cycle. Energy-efficient models with low water usage and energy-saving features can minimize energy consumption.
3. Refrigeration:
- Refrigerators: Refrigerators are constantly running to maintain a cool temperature inside, making them major energy consumers. Newer models with energy-efficient features like adjustable temperature settings and door alarms can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Freezers: Freezers, similar to refrigerators, require continuous energy to maintain freezing temperatures. Energy-efficient models with features like frost-free operation and adjustable temperature settings can contribute to energy savings.
4. Laundry Appliances:
- Washing Machines: Washing machines consume energy for heating water and running the wash cycle. Energy-efficient models with high Energy Star ratings and features like cold water washing and low-speed spin cycles can significantly reduce energy consumption.
- Dryers: Electric dryers consume a considerable amount of energy for heating air to dry clothes. Energy-efficient models with features like heat pump technology and sensor drying can significantly reduce energy consumption.
5. Electronics and Lighting:
- Televisions: Televisions, particularly older models, can consume significant amounts of energy, especially when left on standby mode. Energy-efficient models with LED backlighting and low power consumption ratings can minimize energy consumption.
- Computers and Monitors: Computers and monitors consume energy for running the processor, powering the display, and operating peripherals. Energy-efficient models with power-saving features and energy-efficient monitors can reduce energy consumption.
- Lighting: Traditional incandescent light bulbs are known for their high energy consumption. Replacing them with energy-efficient LED bulbs can significantly reduce energy consumption and lower electricity bills.
Understanding Energy Consumption Measurement Units
- Kilowatt-hour (kWh): This is the standard unit for measuring energy consumption. One kilowatt-hour represents the energy used by a 1000-watt appliance running for one hour.
- BTU (British thermal unit): This unit is commonly used to measure the energy content of fuels like natural gas and oil. One BTU is the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit.
Factors Influencing Energy Consumption
- Appliance Efficiency: Newer appliances often come with energy-efficient features that reduce energy consumption. Look for Energy Star ratings or other certifications indicating energy efficiency.
- Usage Habits: Frequent and prolonged use of appliances can significantly increase energy consumption. Consider adjusting usage patterns, such as reducing shower time or minimizing appliance standby time.
- Climate Conditions: Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can significantly impact energy consumption for heating and cooling systems.
- Household Size: Larger households generally require more energy for heating, cooling, and water heating.
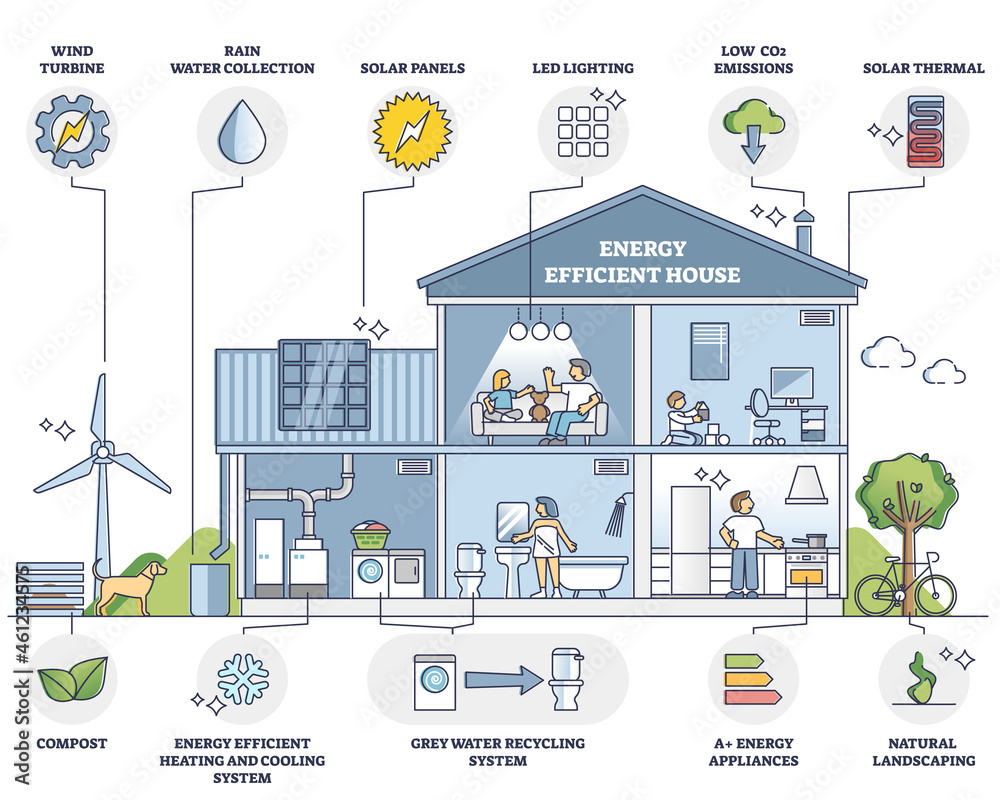
Energy Efficiency Tips for a Greener Home
- Upgrade Appliances: Replace older, less efficient appliances with energy-efficient models. Consider purchasing Energy Star-rated appliances for significant energy savings.
- Optimize Heating and Cooling Systems: Regularly maintain your HVAC system to ensure optimal efficiency. Install programmable thermostats to control temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
- Reduce Water Heating Costs: Install low-flow showerheads and faucets to reduce water usage. Consider upgrading to a tankless water heater for greater efficiency.
- Unplug Devices: Unplug unused electronics and appliances to eliminate phantom load, which is energy consumed even when devices are not in use.
- Use Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED bulbs for significant energy savings and a longer lifespan.
- Practice Energy-Conscious Habits: Turn off lights when leaving rooms, wash clothes in cold water, and air-dry clothes whenever possible.
FAQs About Household Energy Consumption
Q: How much energy does a refrigerator use per month?
A: A typical refrigerator consumes approximately 100-200 kWh per month, depending on its size, efficiency, and usage habits.
Q: How much energy does a washing machine use per load?
A: A washing machine typically uses 1-2 kWh per load, depending on the water temperature and cycle length.
Q: How much energy does a dryer use per load?
A: A dryer can consume 2-4 kWh per load, depending on the type of dryer and the drying time.
Q: How much energy does a television use per day?
A: A television can consume 0.1-0.5 kWh per day, depending on the screen size and usage time.
Q: How can I reduce my home’s energy consumption?
A: Implement energy-efficiency measures like upgrading appliances, optimizing HVAC systems, and practicing energy-conscious habits.
Conclusion
Understanding how much energy our household items consume is crucial for making informed decisions about energy efficiency and reducing our environmental impact. By embracing energy-saving practices, we can minimize our energy footprint, save money on utility bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future.




Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding the Energy Footprint of Our Homes: A Comprehensive Guide to Household Energy Consumption. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply