Understanding Household Energy Consumption: A Guide To Efficient Living
Understanding Household Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficient Living
Related Articles: Understanding Household Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficient Living
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to Understanding Household Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficient Living. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Household Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficient Living

The modern home is a tapestry of interconnected systems, each powered by electricity. From the refrigerator preserving our food to the television providing entertainment, our daily lives are intertwined with the flow of energy. Understanding how much electricity each appliance consumes is crucial for managing energy costs, minimizing environmental impact, and maximizing efficiency.
A Breakdown of Energy Consumption by Appliance
The energy consumption of household appliances varies significantly based on factors like size, age, efficiency rating, and usage patterns. Here’s a breakdown of common appliances and their typical energy consumption:
1. Refrigeration and Freezing:
Refrigerators and freezers are among the most energy-intensive appliances in a home. The average refrigerator consumes around 350-700 kilowatt-hours (kWh) per year, while a freezer can consume 200-500 kWh annually. Modern models with Energy Star ratings are significantly more efficient, consuming up to 25% less energy than older models.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Size: Larger refrigerators and freezers naturally consume more energy.
- Temperature Setting: Setting the temperature too low or too high can lead to increased energy consumption.
- Door Opening Frequency: Frequent door openings allow cold air to escape, requiring the appliance to work harder.
- Location: Placing the refrigerator in a warm environment can increase energy usage.
2. Cooking Appliances:
Ovens, stoves, microwaves, and cooktops contribute significantly to household energy consumption.
-
Ovens: Electric ovens typically consume 2,000-4,000 watts during operation, while gas ovens consume less energy but emit greenhouse gases.
-
Stoves: Electric stovetops consume around 1,200-1,800 watts, while gas stovetops consume less energy.
-
Microwaves: Microwaves are generally energy-efficient, consuming around 700-1,200 watts.
-
Cooktops: Induction cooktops are the most energy-efficient, consuming around 1,500-2,000 watts.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Usage: The frequency and duration of cooking directly impact energy consumption.
- Oven Type: Electric ovens generally consume more energy than gas ovens.
- Cooktop Type: Induction cooktops are more efficient than traditional electric or gas cooktops.
3. Washing and Drying:
Washing machines and clothes dryers consume considerable energy, particularly during heating cycles.
-
Washing Machines: Modern washing machines with Energy Star ratings consume around 150-300 kWh per year.
-
Clothes Dryers: Electric dryers consume around 1,500-2,000 watts during operation, while gas dryers consume less energy.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Water Temperature: Using hot water for washing consumes more energy than using cold water.
- Load Size: Washing full loads of laundry is more efficient than washing small loads.
- Dryer Type: Electric dryers generally consume more energy than gas dryers.
4. Lighting:
Incandescent light bulbs are the least energy-efficient lighting option, while LED bulbs are the most efficient.
-
Incandescent Bulbs: Consume around 60-100 watts.
-
Halogen Bulbs: Consume around 30-75 watts.
-
Compact Fluorescent Bulbs (CFLs): Consume around 10-25 watts.
-
Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Bulbs: Consume around 5-15 watts.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Bulb Type: LED bulbs are the most energy-efficient, followed by CFLs, halogen bulbs, and incandescent bulbs.
- Usage: Leaving lights on unnecessarily increases energy consumption.
5. Entertainment Systems:
Televisions, computers, gaming consoles, and home theaters contribute to household energy consumption.
-
Televisions: Modern LCD and LED TVs consume significantly less energy than older CRT TVs.
-
Computers: Desktop computers consume around 100-300 watts, while laptops consume around 20-50 watts.
-
Gaming Consoles: Consume around 100-200 watts.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Screen Size: Larger screens consume more energy.
- Usage: Leaving devices on standby mode consumes energy unnecessarily.
6. Heating and Cooling:
Heating and cooling systems are major energy consumers, particularly in regions with extreme temperatures.
-
Heating Systems: Electric furnaces consume around 4,000-6,000 watts, while gas furnaces consume less energy.
-
Cooling Systems: Air conditioners consume around 1,000-1,500 watts.
-
Factors Influencing Consumption:
- Climate: Regions with colder or hotter climates require more heating or cooling.
- Home Insulation: Well-insulated homes require less energy for heating and cooling.
- Thermostat Settings: Setting the thermostat appropriately can significantly impact energy consumption.
Understanding the Importance of Energy Consumption
The energy consumption of household appliances has significant implications for both individual finances and environmental sustainability.
1. Financial Implications:
- Energy Bills: Excessive energy consumption translates to higher energy bills, impacting household budgets.
- Savings: By using energy-efficient appliances and reducing unnecessary consumption, households can save money on their energy bills.
2. Environmental Implications:
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: The burning of fossil fuels to generate electricity releases greenhouse gases, contributing to climate change.
- Resource Depletion: The production and operation of appliances require natural resources, which are finite.
- Pollution: The generation of electricity can also lead to air and water pollution.
FAQs
Q: How much electricity does a typical household use annually?
A: The average U.S. household uses around 10,900 kWh of electricity per year. However, this number can vary significantly depending on factors like household size, climate, appliance usage, and energy efficiency practices.
Q: How can I reduce my household energy consumption?
A: There are numerous ways to reduce household energy consumption:
- Upgrade Appliances: Invest in energy-efficient appliances with Energy Star ratings.
- Reduce Usage: Limit the use of energy-intensive appliances like ovens and dryers.
- Turn Off Lights: Make sure to turn off lights when leaving a room.
- Unplug Devices: Unplug electronic devices when not in use to prevent phantom load consumption.
- Adjust Thermostat: Set the thermostat appropriately for heating and cooling, and consider using programmable thermostats.
- Practice Energy-Saving Habits: Wash clothes in cold water, air-dry clothes whenever possible, and use natural light whenever feasible.
Tips for Reducing Household Energy Consumption
- Conduct an Energy Audit: Hire a professional to identify areas of energy waste in your home.
- Install Smart Meters: Monitor your energy consumption in real-time to identify areas for improvement.
- Use Energy-Saving Light Bulbs: Replace traditional incandescent bulbs with LED or CFL bulbs.
- Install Weatherstripping and Caulking: Seal air leaks around windows and doors to improve insulation.
- Plant Trees for Shade: Shade your home from the sun during the summer months to reduce cooling needs.
- Consider Renewable Energy Sources: Explore options like solar panels or wind turbines to generate your own electricity.
Conclusion
Understanding the energy consumption of household appliances is essential for making informed decisions about energy efficiency. By embracing energy-saving practices, we can reduce our environmental impact, save money on energy bills, and contribute to a more sustainable future.

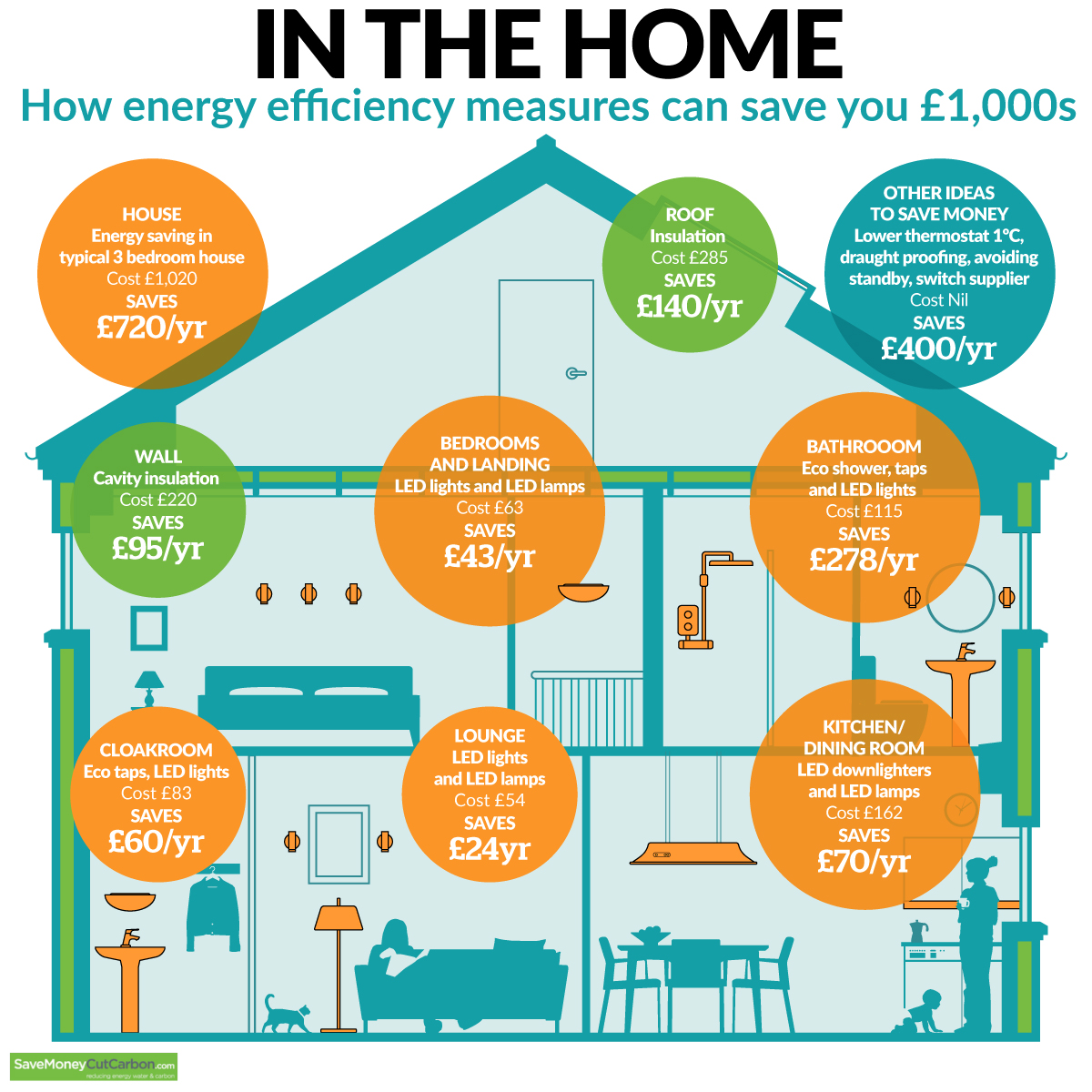

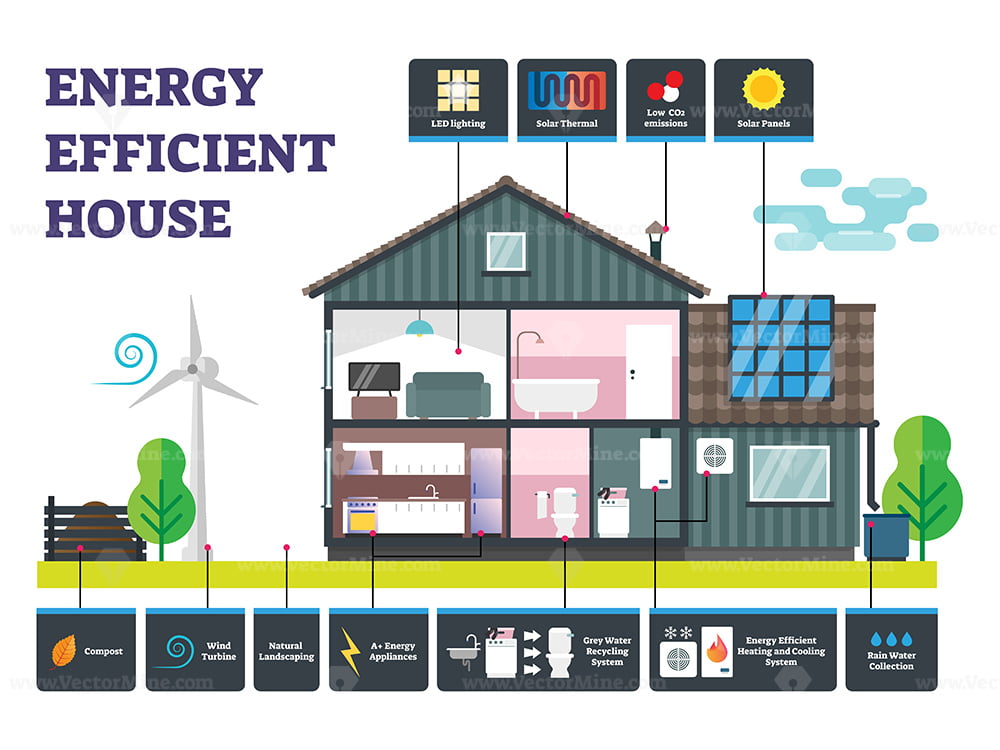

![[Infographic] Energy Efficiency In The Home – Samsung Global Newsroom](https://img.global.news.samsung.com/global/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/Infographic-Energy-Efficiency-In-The-Home1.jpg)

Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Household Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficient Living. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply