Understanding Home Appliance Energy Consumption: A Guide To Efficiency And Savings
Understanding Home Appliance Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficiency and Savings
Related Articles: Understanding Home Appliance Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficiency and Savings
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Home Appliance Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficiency and Savings. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Home Appliance Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficiency and Savings

In the modern world, our homes are filled with a plethora of appliances that make our lives easier and more comfortable. However, these conveniences come at a cost – energy consumption. Understanding the energy demands of our appliances is crucial for managing household expenses, reducing environmental impact, and making informed choices about energy-efficient alternatives. This article provides a comprehensive overview of the power consumption of common household appliances, highlighting their energy requirements and offering practical tips for reducing energy usage.
A Comprehensive List of Appliance Power Consumption:
This section provides a detailed breakdown of the typical power consumption of various appliances found in a modern home. The values provided are approximations, and actual consumption may vary based on factors such as appliance model, usage patterns, and efficiency ratings.
1. Major Appliances:
-
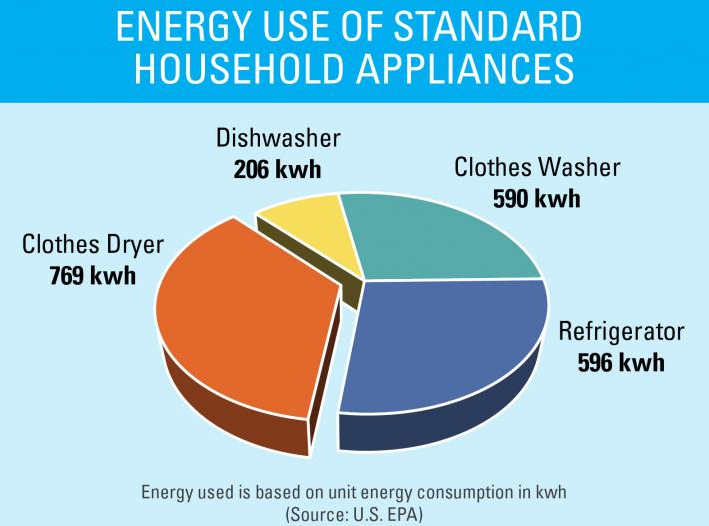
Refrigerator:
- Average Power Consumption: 150-700 watts (varies significantly based on size, features, and efficiency)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 400-1,500 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Size, temperature settings, door opening frequency, and defrosting method.
-
Freezer:
- Average Power Consumption: 100-300 watts (varies based on size, features, and efficiency)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 200-700 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Size, temperature settings, door opening frequency, and defrosting method.
-
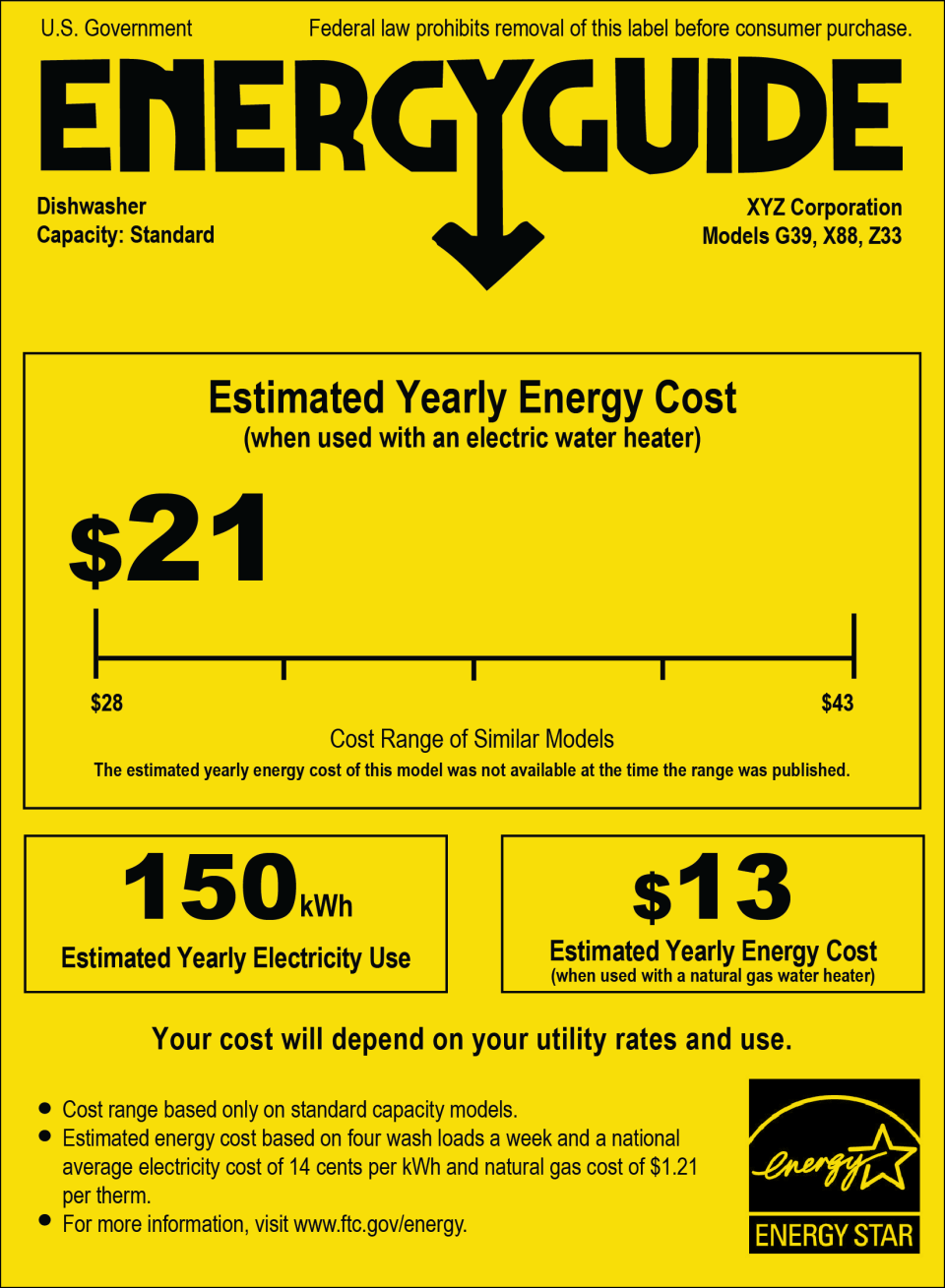
Dishwasher:
- Average Power Consumption: 1,200-1,800 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 200-400 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Water temperature, wash cycle length, and load size.
-
Washing Machine:
- Average Power Consumption: 300-500 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 100-300 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Water temperature, wash cycle length, and load size.
-
Clothes Dryer:
- Average Power Consumption: 2,000-5,000 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 1,000-2,000 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Load size, drying temperature, and type of dryer (electric vs. gas).
-
Oven:
- Average Power Consumption: 2,000-5,000 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 200-600 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Oven size, temperature settings, and usage frequency.
-
Microwave Oven:
- Average Power Consumption: 700-1,200 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 50-150 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Power level, heating time, and usage frequency.
-
Electric Water Heater:
- Average Power Consumption: 4,500 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 4,000-8,000 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Water heater size, temperature settings, and water usage patterns.
-
Air Conditioner:
- Average Power Consumption: 1,000-5,000 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 1,000-4,000 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: AC size, temperature settings, and usage frequency.
2. Smaller Appliances:
-
Television:
- Average Power Consumption: 50-200 watts (varies based on screen size and technology)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 100-400 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Screen size, brightness settings, and usage frequency.
-
Computer:
- Average Power Consumption: 100-300 watts (varies based on model and usage)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 100-300 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Processor speed, RAM, and usage patterns.
-
Coffee Maker:
- Average Power Consumption: 800-1,200 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 20-50 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Size, brewing time, and usage frequency.
-
Toaster:
- Average Power Consumption: 800-1,200 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 10-30 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Power level and usage frequency.
-
Blender:
- Average Power Consumption: 300-700 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 10-30 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Power level and usage frequency.
-
Hair Dryer:
- Average Power Consumption: 1,000-1,800 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 10-30 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Power level and usage frequency.
-
Iron:
- Average Power Consumption: 1,000-1,500 watts (during operation)
- Annual Energy Consumption: 10-30 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Power level and usage frequency.
3. Lighting:
-
Incandescent Light Bulb:
- Average Power Consumption: 40-100 watts
- Annual Energy Consumption: 10-50 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Bulb wattage and usage frequency.
-
Compact Fluorescent Light Bulb (CFL):
- Average Power Consumption: 5-15 watts
- Annual Energy Consumption: 1-5 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Bulb wattage and usage frequency.
-
LED Light Bulb:
- Average Power Consumption: 1-10 watts
- Annual Energy Consumption: 0.5-5 kWh
- Factors Affecting Consumption: Bulb wattage and usage frequency.
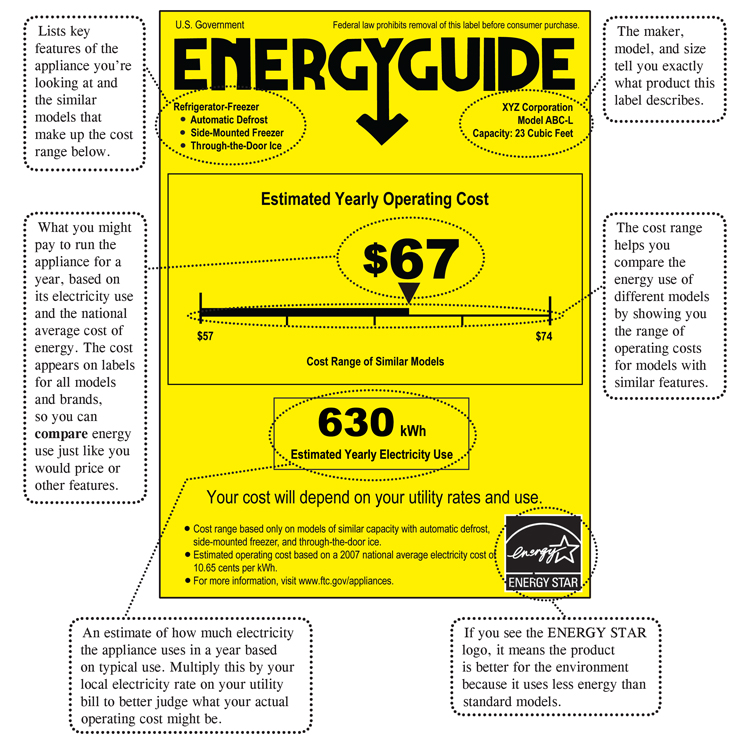
The Importance of Understanding Appliance Energy Consumption:
Understanding appliance energy consumption offers numerous benefits, including:
- Reduced Energy Bills: By identifying high-energy consuming appliances and adopting energy-saving practices, households can significantly reduce their electricity bills.
- Environmental Sustainability: Reducing energy consumption translates to lower carbon emissions, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
- Informed Appliance Purchases: Knowledge about energy consumption empowers consumers to make informed choices when purchasing new appliances, opting for models with higher energy efficiency ratings.
- Energy Conservation Awareness: Understanding appliance energy usage fosters a sense of responsibility and encourages the adoption of energy-saving habits within the household.
FAQs about Appliance Energy Consumption:
1. How can I determine the energy consumption of my appliances?
Most appliances have an energy label that provides information about their energy consumption. You can also consult the user manual or manufacturer website for details.
2. What are energy efficiency ratings, and how do they help?
Energy efficiency ratings, such as the Energy Star label, indicate the relative energy efficiency of an appliance. Appliances with higher efficiency ratings consume less energy for the same level of performance.
3. How can I reduce my appliance energy consumption?
- Use Energy-Efficient Appliances: Opt for appliances with high energy efficiency ratings.
- Unplug Appliances When Not in Use: Even when turned off, some appliances continue to draw power.
- Adjust Appliance Settings: Optimize temperature settings on refrigerators, dishwashers, and washing machines.
- Use Appliances Efficiently: Avoid overfilling dishwashers and washing machines, and utilize the appropriate settings for your needs.
- Choose Energy-Efficient Lighting: Replace incandescent bulbs with CFLs or LEDs.
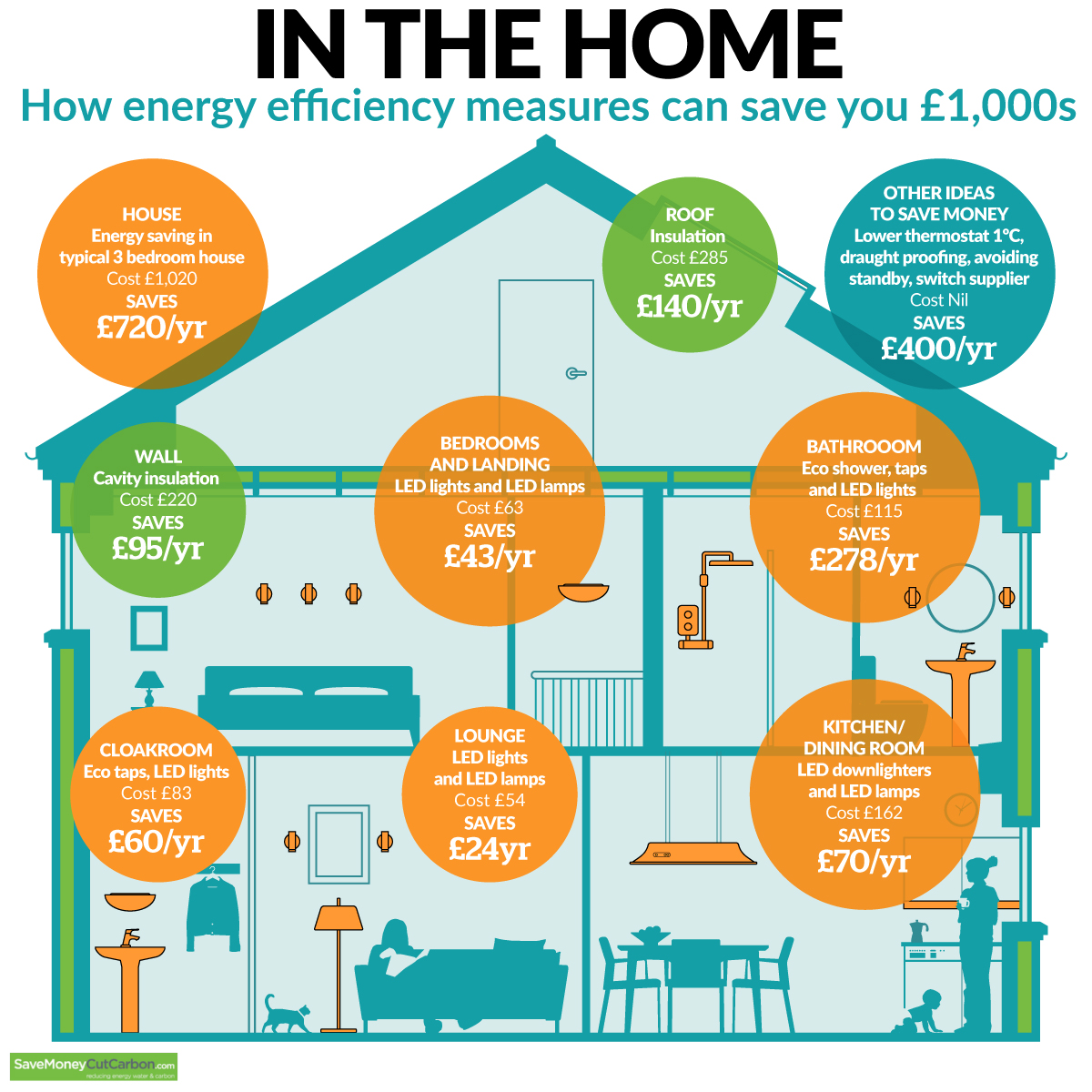
Tips for Reducing Appliance Energy Consumption:
- Refrigerator: Ensure the refrigerator door seals properly, keep the coils clean, and avoid overcrowding the shelves.
- Freezer: Keep the freezer full, as a full freezer requires less energy to maintain temperature.
- Dishwasher: Wash full loads, use air-dry settings, and avoid pre-rinsing dishes.
- Washing Machine: Wash clothes in cold water and air-dry them whenever possible.
- Clothes Dryer: Use the dryer only when necessary, and consider using a clothesline for drying.
- Oven: Use the oven’s self-cleaning cycle only when necessary, and utilize smaller appliances like toasters and microwaves for heating.
- Microwave Oven: Use the microwave for reheating and small cooking tasks, as it consumes less energy than an oven.
- Electric Water Heater: Lower the water heater temperature to 120 degrees Fahrenheit.
- Air Conditioner: Use a programmable thermostat, and keep windows and doors closed when the AC is running.
- Television: Turn off the TV when not in use, and utilize energy-saving modes.
- Computer: Shut down the computer when not in use, and use energy-saving settings.
- Coffee Maker: Use a coffee maker with an automatic shut-off feature.
- Toaster: Use a toaster oven instead of a traditional toaster for larger baking tasks.
- Blender: Use a blender with a variable speed setting, and choose the appropriate speed for your blending needs.
- Hair Dryer: Use a hair dryer with a low heat setting, and air-dry your hair whenever possible.
- Iron: Use an iron with a steam setting, as it consumes less energy than a dry iron.
Conclusion:
Understanding appliance energy consumption is essential for managing household expenses, reducing environmental impact, and making informed decisions about energy-efficient products. By adopting energy-saving practices and utilizing appliances efficiently, households can significantly reduce their energy consumption, contribute to a sustainable future, and save money on their energy bills.



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Home Appliance Energy Consumption: A Guide to Efficiency and Savings. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply