Understanding Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview
Understanding Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview
Related Articles: Understanding Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview

Explosives are substances that undergo rapid chemical reactions, releasing a large amount of energy in a short period, creating a sudden expansion of volume. This expansion generates a shockwave, capable of causing significant destruction. Explosives have a wide range of applications, from industrial mining and construction to military operations and even fireworks. However, their potential for harm necessitates careful handling and strict regulations.
This article will delve into the characteristics, classifications, and applications of common explosives, providing a comprehensive understanding of these powerful substances.
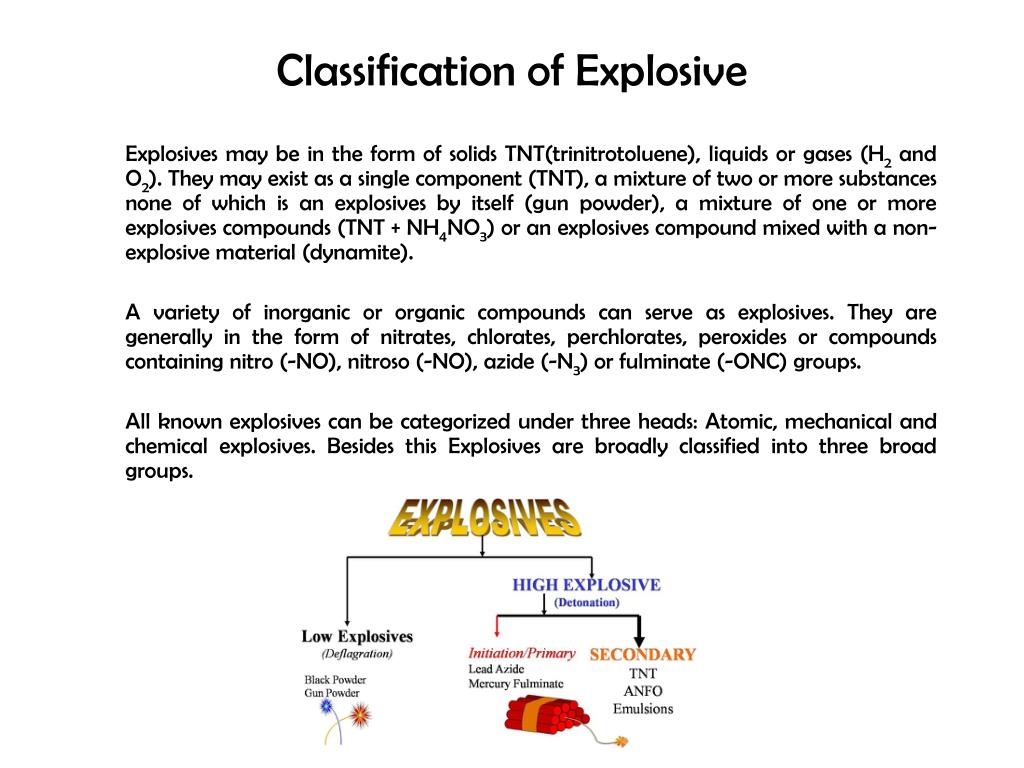
Classification of Explosives
Explosives are typically classified based on their sensitivity, detonation velocity, and chemical composition.
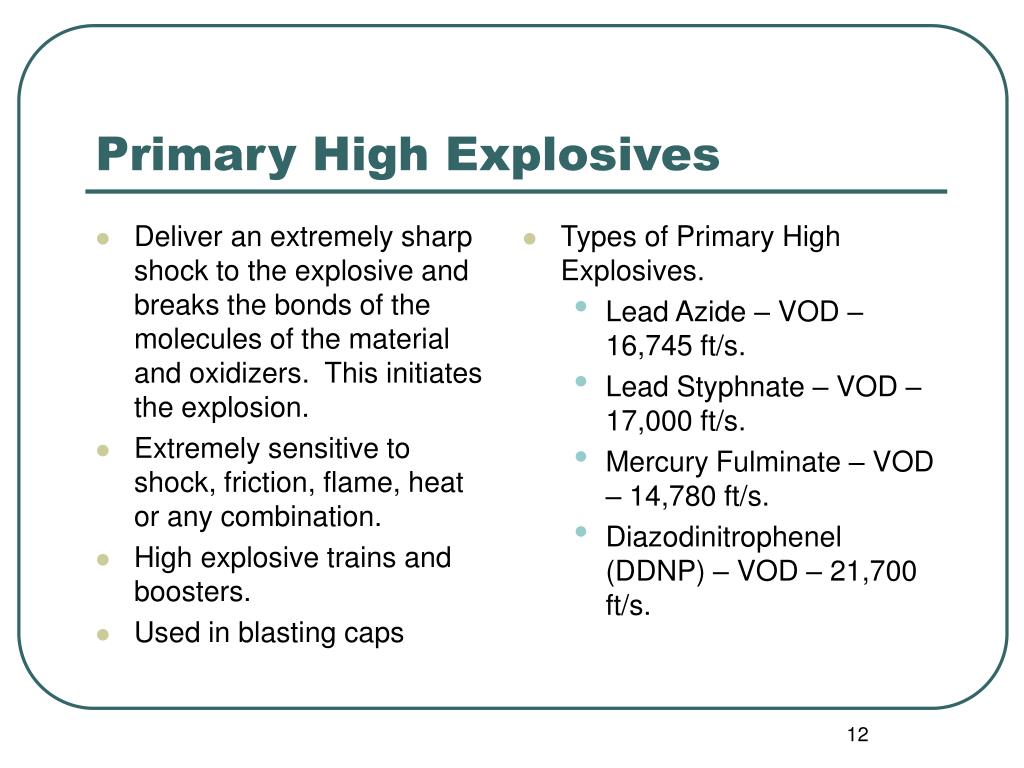
1. Primary Explosives:
Primary explosives are highly sensitive to initiation, detonating with minimal external stimuli like heat, friction, or impact. They are often used as detonators to initiate the explosion of less sensitive explosives. Examples include:
- Mercury Fulminate (Hg(CNO)2): This highly sensitive compound was historically used in percussion caps, but its toxicity has led to its replacement in many applications.
- Lead Azide (Pb(N3)2): Lead azide is another sensitive primary explosive used in detonators due to its reliability and stability.
- Diazodinitrophenol (DDNP): DDNP is a powerful primary explosive, but its sensitivity requires careful handling.
2. Secondary Explosives:
Secondary explosives are less sensitive than primary explosives and require a detonator to initiate their explosion. They are generally more stable and safer to handle, making them suitable for various applications. Examples include:
- Dynamite (Nitroglycerin absorbed in a porous material): Dynamite is a classic explosive widely used in mining, construction, and demolition. Its sensitivity is reduced by absorbing nitroglycerin into a stable material like sawdust or diatomaceous earth.
- Ammonium Nitrate Fuel Oil (ANFO): ANFO is a widely used explosive mixture of ammonium nitrate and fuel oil. Its low cost and ease of preparation make it a popular choice for mining and quarrying.
- RDX (Cyclotrimethylenetrinitramine): RDX is a powerful and versatile explosive used in military applications and some commercial explosives.
- PETN (Pentaerythritol tetranitrate): PETN is a powerful and stable explosive used in detonators, shaped charges, and military applications.
- TNT (Trinitrotoluene): TNT is a well-known explosive, stable and relatively insensitive to shock and friction. It is used in military applications and some industrial explosives.
3. Tertiary Explosives:
Tertiary explosives are the least sensitive and require a significant amount of energy to detonate. They are often used in large-scale blasting operations and are generally considered safer to handle than primary and secondary explosives. Examples include:
- Ammonium Nitrate (NH4NO3): Ammonium nitrate is a common fertilizer and a key component in many explosives. Its sensitivity is low, requiring a detonator to initiate an explosion.
- Black Powder (Mixture of charcoal, sulfur, and potassium nitrate): Black powder is a historic explosive, used in firearms, fireworks, and other applications. Its low detonation velocity makes it unsuitable for high-performance applications.
Applications of Explosives
Explosives play a crucial role in various industries and sectors, contributing to economic growth and development. Some of the key applications include:
- Mining and Quarrying: Explosives are essential for extracting valuable minerals and ores from the earth. They are used to break up large rock formations, facilitating efficient mining operations.
- Construction and Demolition: Explosives are used in large-scale construction projects for controlled demolition of buildings and structures. They are also used to excavate tunnels and create foundations.
- Military Applications: Explosives are a cornerstone of military operations, used in weapons, ammunition, and demolition charges.
- Fireworks: Fireworks rely on the controlled explosion of pyrotechnic compositions, creating spectacular visual displays.
- Scientific Research: Explosives are used in research and development of new materials, processes, and technologies.
Safety Considerations
Explosives are inherently dangerous substances, requiring strict safety precautions during handling, storage, and transportation.
- Storage: Explosives should be stored in secure, well-ventilated locations, away from heat, ignition sources, and incompatible materials.
- Handling: Only trained and authorized personnel should handle explosives, following established safety procedures and wearing appropriate protective gear.
- Transportation: Explosives must be transported in designated vehicles with specialized safety features, adhering to strict regulations and guidelines.
- Disposal: The disposal of explosives must be handled by qualified professionals, ensuring safe and environmentally responsible practices.
FAQs about Explosives
Q: What is the difference between an explosion and a detonation?
A: An explosion is a rapid expansion of volume due to the release of energy, while a detonation is a supersonic explosion characterized by a shockwave propagating through the explosive material.
Q: What are the dangers of explosives?
A: Explosives pose significant dangers, including:
- Detonation: Uncontrolled detonation can cause significant damage, injury, or even death.
- Fire: Explosives can ignite fires, posing a risk to life and property.
- Toxic fumes: Some explosives release toxic fumes upon detonation, posing health hazards.
Q: How are explosives controlled?
A: Explosives are strictly regulated by government agencies to ensure safety and prevent misuse. These regulations include:
- Licensing: Individuals and organizations handling explosives must obtain licenses and permits.
- Storage and transportation: Strict regulations govern the storage and transportation of explosives.
- Security: Explosives are stored in secure locations with access control measures.
Q: How can I learn more about explosives?
A: You can learn more about explosives through:
- Government agencies: The Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) in the United States provides comprehensive information on explosives.
- Professional organizations: Organizations like the National Safety Council (NSC) offer resources and training on explosives safety.
- Educational institutions: Universities and colleges offer courses and programs related to explosives and their applications.
Tips for Handling Explosives
- Never handle explosives without proper training and authorization.
- Always follow established safety procedures and guidelines.
- Store explosives in secure and well-ventilated locations.
- Keep explosives away from heat, ignition sources, and incompatible materials.
- Transport explosives in designated vehicles with specialized safety features.
- Dispose of explosives responsibly through qualified professionals.
Conclusion
Explosives are powerful substances with a wide range of applications, from industrial processes to military operations. Their potential for both good and harm necessitates a deep understanding of their characteristics, classifications, and safe handling practices. By following established regulations and safety protocols, we can harness the power of explosives for beneficial purposes while minimizing risks.
It is crucial to remember that the misuse of explosives can have devastating consequences. Responsible handling and ethical application are paramount to ensuring the safe and efficient use of these powerful substances.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Explosives: A Comprehensive Overview. We hope you find this article informative and beneficial. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply