Understanding Alpha Particles: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding Alpha Particles: A Comprehensive Guide
Related Articles: Understanding Alpha Particles: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to Understanding Alpha Particles: A Comprehensive Guide. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
Understanding Alpha Particles: A Comprehensive Guide
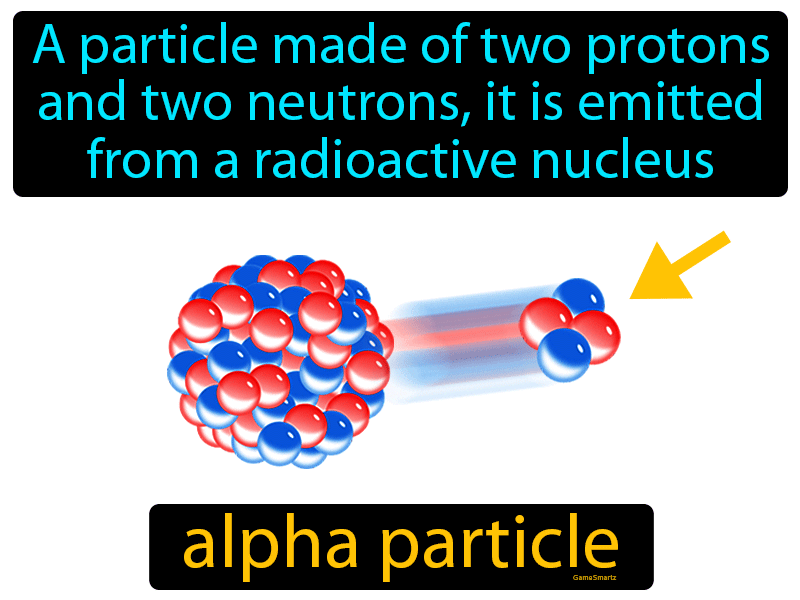
Alpha particles, often denoted as α particles, are a fundamental component of nuclear physics and play a crucial role in various natural phenomena and technological applications. Understanding their nature, properties, and interactions is essential for comprehending the intricacies of radioactive decay, nuclear reactions, and the broader field of nuclear science.
This comprehensive guide provides an in-depth exploration of alpha particles, delving into their structure, properties, interactions, and applications. It aims to offer a clear and informative overview of this essential concept, catering to individuals with diverse backgrounds and levels of understanding.
1. Structure and Composition
Alpha particles are essentially helium nuclei, consisting of two protons and two neutrons tightly bound together. This structure gives them a positive charge of +2e (twice the charge of a proton) and a mass number of 4 (equal to the sum of protons and neutrons).
2. Origin and Emission
Alpha particles are primarily emitted during a type of radioactive decay known as alpha decay. This process occurs when an unstable atomic nucleus undergoes transformation, releasing an alpha particle and transforming into a new nucleus with a lower atomic number and mass number.
3. Properties of Alpha Particles
- High Energy: Alpha particles possess significant kinetic energy due to their strong nuclear binding. This energy is a direct consequence of the strong force holding the nucleons together.
- High Ionization Potential: Due to their charge and mass, alpha particles interact strongly with matter, causing significant ionization. This ionization occurs when the alpha particle strips electrons from atoms it encounters, leaving a trail of ions in its wake.
- Short Range: Despite their high energy, alpha particles have a relatively short range in matter. Their large mass and charge lead to frequent collisions, causing them to lose energy quickly.
- Low Penetration Power: The high ionization potential and short range limit the penetration power of alpha particles. They can be effectively stopped by a thin sheet of paper or a few centimeters of air.
4. Interactions with Matter
Alpha particles primarily interact with matter through ionization and excitation. These interactions can be summarized as follows:
- Ionization: Alpha particles collide with atoms, stripping electrons and creating ions. This process is the primary mechanism by which alpha particles deposit their energy in matter.
- Excitation: Alpha particles can also excite atoms, raising them to higher energy levels. This excitation can lead to the emission of photons (light) as the atoms return to their ground state.
- Nuclear Reactions: In specific cases, alpha particles can interact with atomic nuclei, leading to nuclear reactions. These reactions can result in the emission of other particles, such as protons, neutrons, or gamma rays.
5. Applications of Alpha Particles
The unique properties of alpha particles have led to their application in various fields:
- Nuclear Medicine: Alpha particle emitters are used in targeted alpha therapy (TAT) for treating cancer. These emitters are attached to molecules that specifically bind to cancer cells, delivering a highly localized dose of radiation.
- Smoke Detectors: Americium-241, an alpha emitter, is used in smoke detectors. When smoke particles enter the detector, they absorb alpha particles, reducing the ionization current and triggering an alarm.
- Static Eliminators: Alpha emitters can be used to neutralize static charges on surfaces. This is achieved by ionizing the surrounding air, reducing the build-up of static electricity.
- Radioactive Dating: Alpha decay is used in radioactive dating techniques to determine the age of rocks, fossils, and other ancient artifacts. By measuring the ratio of parent isotopes to daughter isotopes, scientists can estimate the time elapsed since the material’s formation.
6. Health Effects of Alpha Particles
Alpha particles pose a significant health risk if they enter the body. Due to their high ionization potential, they can damage DNA and other cellular components, leading to various health problems, including:
- Cancer: Exposure to alpha radiation can increase the risk of developing cancer, particularly lung cancer, bone cancer, and leukemia.
- Radiation Sickness: High doses of alpha radiation can cause radiation sickness, characterized by symptoms like nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and hair loss.
- Genetic Damage: Alpha particles can damage DNA, potentially leading to mutations and genetic disorders.
7. Safety Precautions
It is crucial to handle alpha emitters with appropriate safety precautions to minimize exposure:
- Shielding: Alpha particles can be effectively shielded by thin materials like paper or a few centimeters of air.
- Distance: Maintaining distance from alpha sources reduces exposure as the intensity of radiation decreases with distance.
- Ventilation: Proper ventilation helps to disperse alpha particles, reducing their concentration in the air.
- Personal Protective Equipment: Gloves, respirators, and protective clothing should be worn when handling alpha sources.
FAQs about Alpha Particles
Q: What are the differences between alpha, beta, and gamma radiation?
A: Alpha, beta, and gamma radiation are different types of ionizing radiation. Alpha particles are helium nuclei, beta particles are electrons or positrons, and gamma rays are high-energy photons. Alpha particles have the highest ionization potential but the shortest range, while gamma rays have the lowest ionization potential but the longest range.
Q: How are alpha particles used in cancer treatment?
A: Alpha particles are used in targeted alpha therapy (TAT) to deliver a high dose of radiation directly to cancer cells. Alpha emitters are attached to molecules that specifically bind to cancer cells, delivering a highly localized dose of radiation that effectively destroys the cancerous cells while minimizing damage to surrounding healthy tissues.
Q: Are alpha particles dangerous?
A: Alpha particles can be dangerous if they enter the body. Due to their high ionization potential, they can damage DNA and other cellular components, increasing the risk of cancer and other health problems. However, alpha particles are easily shielded by thin materials like paper or a few centimeters of air.
Q: What are some examples of alpha emitters?
A: Some common examples of alpha emitters include:
- Uranium-238: Found naturally in the Earth’s crust.
- Radium-226: Used in luminous paint and medical treatments.
- Polonium-210: Found in tobacco smoke and is a major contributor to lung cancer.
- Americium-241: Used in smoke detectors.
Tips for Understanding Alpha Particles
- Visualize the structure: Imagine an alpha particle as a tiny helium nucleus, composed of two protons and two neutrons tightly bound together.
- Connect the concepts: Understand how alpha particles are produced through alpha decay and how their properties influence their interactions with matter.
- Explore applications: Learn about the various applications of alpha particles in medicine, technology, and research.
- Consider the safety implications: Be aware of the potential health risks associated with alpha radiation and take appropriate safety precautions when handling alpha emitters.
Conclusion
Alpha particles are a fundamental component of nuclear physics with significant implications for our understanding of radioactive decay, nuclear reactions, and the broader field of nuclear science. Their unique properties, including high energy, high ionization potential, and short range, have led to their application in various fields, from cancer treatment to smoke detection. Understanding the nature, properties, and interactions of alpha particles is essential for comprehending the intricacies of nuclear phenomena and for ensuring safe handling of radioactive materials. Continued research and innovation in this area will undoubtedly lead to further advancements in various fields, benefiting humanity in countless ways.






Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into Understanding Alpha Particles: A Comprehensive Guide. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension

.PNG)
Leave a Reply