The Invisible Network: How Radio Waves Power Our World
The Invisible Network: How Radio Waves Power Our World
Related Articles: The Invisible Network: How Radio Waves Power Our World
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate through the intriguing topic related to The Invisible Network: How Radio Waves Power Our World. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Invisible Network: How Radio Waves Power Our World

Radio waves, a type of electromagnetic radiation, are an integral part of modern life, shaping communication, entertainment, navigation, and even our understanding of the universe. Though invisible to the naked eye, these waves carry information across vast distances, enabling a myriad of technologies that have transformed the way we live, work, and interact with the world.
Unveiling the Invisible: The Nature of Radio Waves
Radio waves, like visible light, are part of the electromagnetic spectrum, a range of energy waves that travel at the speed of light. They differ from visible light in their wavelength, which is significantly longer. This longer wavelength allows radio waves to penetrate obstacles like walls and foliage, making them ideal for long-distance communication.
From Broadcasting to Beyond: Applications of Radio Waves
The applications of radio waves are vast and diverse, spanning a wide range of fields:
1. Communication and Broadcasting:
- Radio Broadcasting: Radio waves are the backbone of traditional radio broadcasting, transmitting audio signals to receivers like radios and smartphones. This technology, dating back to the early 20th century, continues to play a vital role in news dissemination, entertainment, and public safety announcements.
- Television Broadcasting: Television signals, carrying both audio and video information, are also transmitted via radio waves. This technology, pioneered in the mid-20th century, has revolutionized entertainment and information access.
- Cellular Communication: Mobile phones rely on radio waves to connect to cellular towers, enabling voice calls, text messaging, and data transmission. The ubiquity of mobile phones has transformed communication, allowing people to connect instantly across vast distances.
- Wi-Fi and Bluetooth: These wireless technologies utilize radio waves to establish local area networks, enabling devices like computers, smartphones, and tablets to communicate with each other without the need for physical cables.
2. Navigation and Positioning:
- GPS (Global Positioning System): GPS satellites constantly transmit radio signals that are received by GPS receivers, allowing precise location determination. This technology is essential for navigation, mapping, and numerous other applications, including transportation, surveying, and tracking.
- Radio Navigation Systems: Ships, aircraft, and other vehicles utilize radio navigation systems like VOR (Very High Frequency Omnidirectional Range) and NDB (Non-Directional Beacon) to determine their position and course. These systems are vital for safe and efficient navigation, particularly in remote or challenging environments.
3. Remote Sensing and Data Collection:
- Satellite Communication: Satellites use radio waves to transmit data and signals to and from Earth, enabling communication, navigation, weather forecasting, and Earth observation. This technology plays a critical role in various fields, including telecommunications, environmental monitoring, and disaster management.
- Radio Astronomy: Astronomers use radio telescopes to detect and analyze radio waves emitted by celestial objects, providing valuable insights into the composition, structure, and evolution of the universe. These observations have led to groundbreaking discoveries about the origins of the universe, the formation of stars and galaxies, and the existence of exoplanets.
4. Medical Applications:
- Medical Imaging: Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) utilizes radio waves and magnetic fields to create detailed images of the inside of the human body. MRI is a powerful diagnostic tool used to detect and diagnose a wide range of conditions, including tumors, injuries, and neurological disorders.
- Radiotherapy: Radio waves can be used to treat cancer by targeting and destroying cancerous cells. This therapy, known as radiotherapy, is a vital part of cancer treatment, offering effective and precise tumor eradication.
5. Industrial and Scientific Applications:
- Radio Frequency Identification (RFID): RFID tags use radio waves to transmit information about objects, enabling tracking and identification in various applications, including inventory management, supply chain logistics, and security systems.
- Microwave Ovens: Microwave ovens utilize radio waves to heat food by exciting water molecules. This technology provides a convenient and efficient method for cooking and reheating food.
- Remote Control Systems: Radio waves are used in remote control systems for devices like televisions, garage door openers, and toys. This technology allows users to control devices remotely, providing convenience and flexibility.
FAQs: Addressing Common Questions about Radio Waves
Q: Are radio waves harmful to human health?
A: Radio waves are a form of non-ionizing radiation, meaning they do not have enough energy to break chemical bonds or damage DNA. While prolonged exposure to high levels of radio waves can cause heating effects, the levels used in everyday devices are generally considered safe. Regulatory bodies worldwide set limits on radio wave exposure to ensure public safety.
Q: How do radio waves travel through space?
A: Radio waves, like other electromagnetic waves, travel through space at the speed of light. They do not require a medium to propagate, unlike sound waves which need air or water to travel.
Q: Can radio waves be blocked?
A: Yes, radio waves can be blocked by certain materials, including metals, water, and dense concrete. The effectiveness of a material in blocking radio waves depends on its thickness and conductivity.
Q: What is the difference between radio waves and microwaves?
A: Radio waves and microwaves are both forms of electromagnetic radiation, but they differ in their frequency and wavelength. Microwaves have a higher frequency and shorter wavelength than radio waves. This difference in frequency allows microwaves to be used for heating food, while radio waves are used for communication and other applications.
Tips: Understanding and Utilizing Radio Waves
- Be aware of radio wave exposure: While radio waves are generally considered safe, it’s important to be mindful of prolonged exposure to high levels, particularly from devices like cell phones and Wi-Fi routers.
- Use radio wave blocking materials: If you need to shield sensitive equipment or areas from radio waves, consider using materials like metal or conductive paint.
- Optimize radio wave reception: To improve radio wave reception, ensure clear line-of-sight between the transmitter and receiver, and minimize obstacles like walls and metal objects.
- Understand the limitations of radio wave communication: Radio waves can be affected by factors like atmospheric conditions, interference, and distance, which can impact signal strength and reliability.
Conclusion: The Power and Promise of Radio Waves
Radio waves, despite their invisibility, have become an integral part of our modern world, enabling communication, navigation, entertainment, and scientific exploration. Their versatility and ability to travel vast distances make them an indispensable tool for a wide range of applications. As technology continues to evolve, radio waves will likely play an even more prominent role in shaping our future, unlocking new possibilities and driving innovation across various fields.


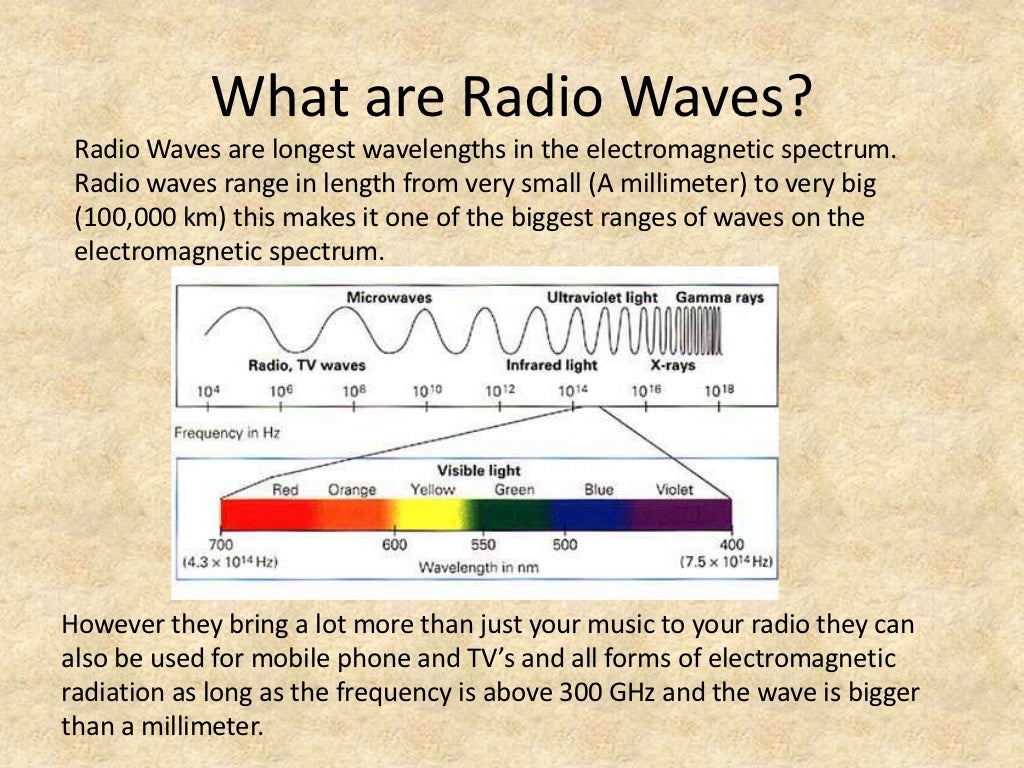



Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Invisible Network: How Radio Waves Power Our World. We appreciate your attention to our article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply