The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through The Waves
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through the Waves
Related Articles: The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through the Waves
Introduction
In this auspicious occasion, we are delighted to delve into the intriguing topic related to The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through the Waves. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through the Waves

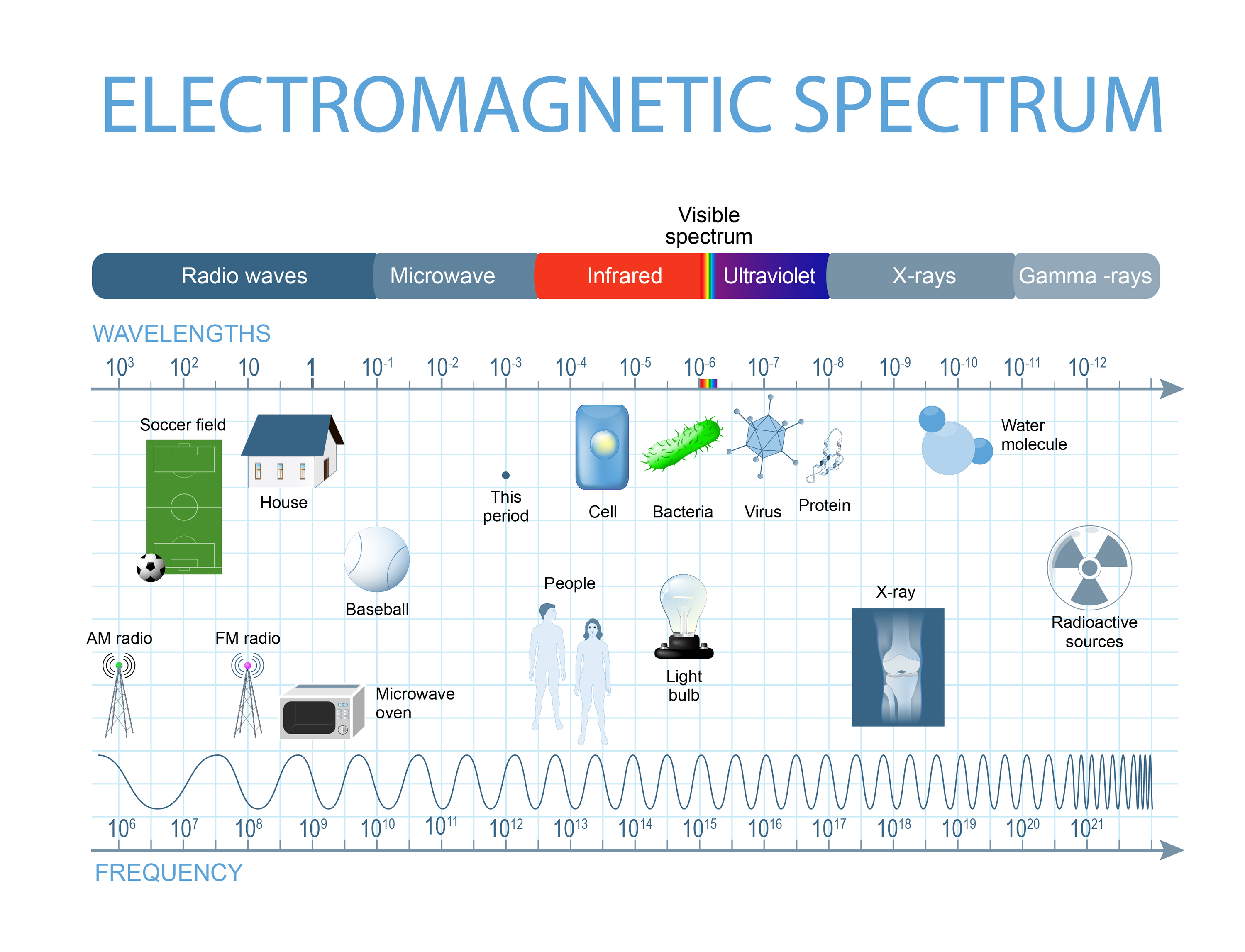
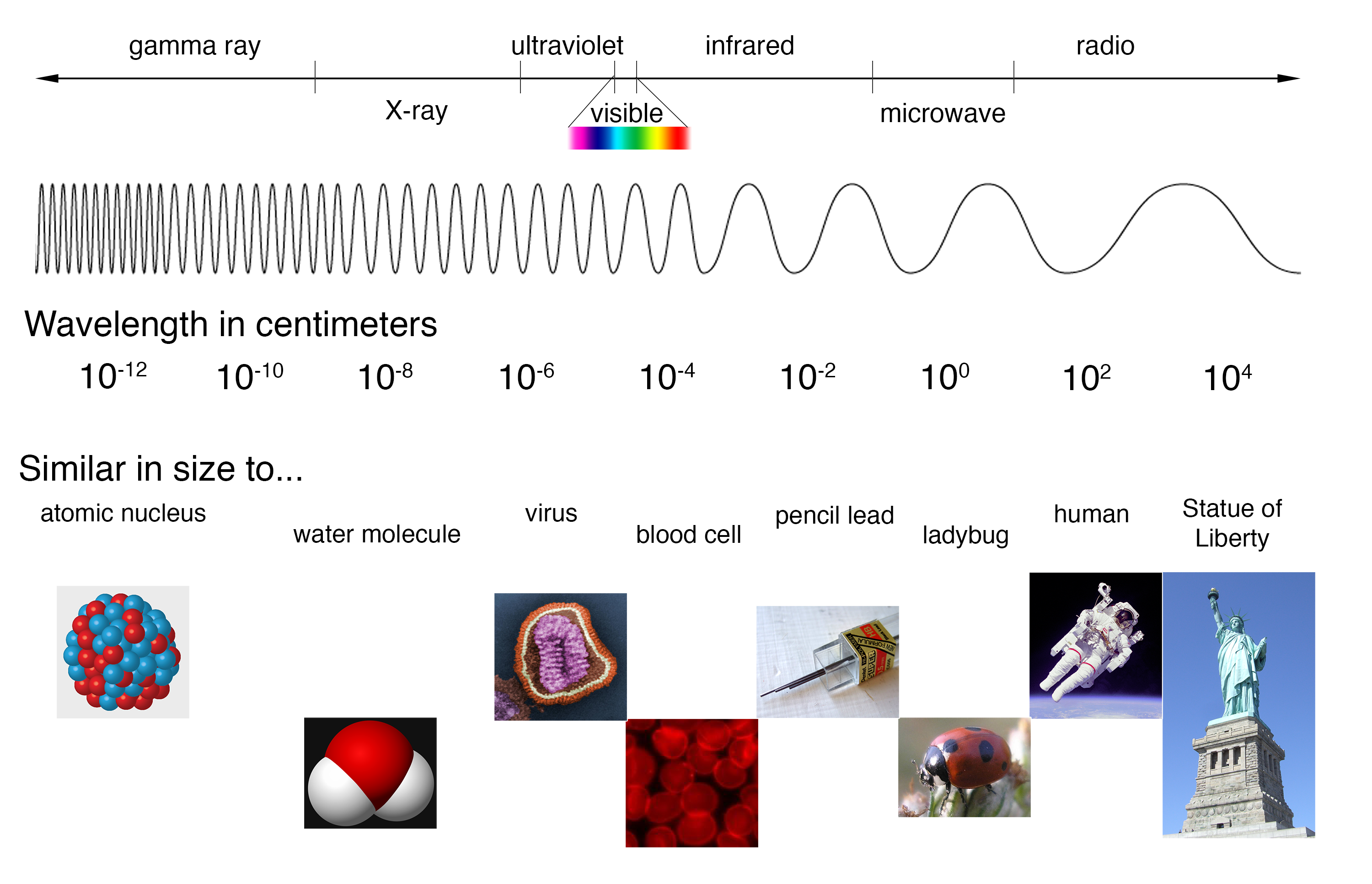
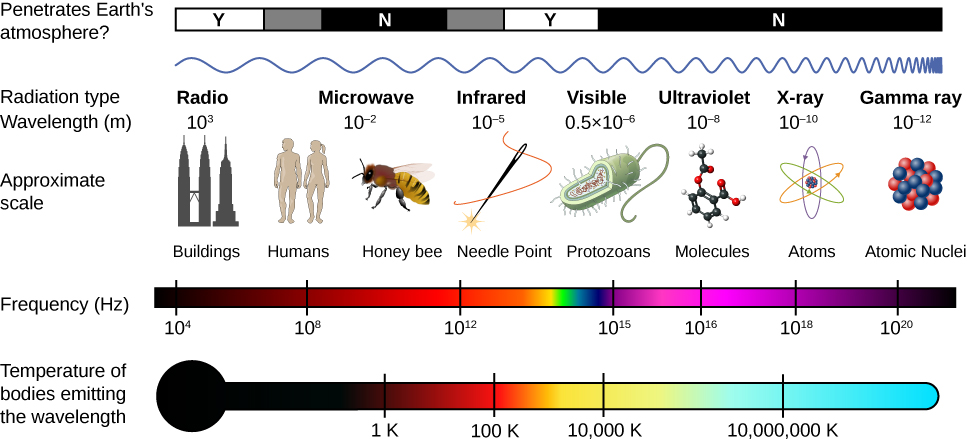
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast and fascinating landscape, encompassing a wide range of radiation, from the incredibly low-energy radio waves to the highly energetic gamma rays. This spectrum, characterized by its wave-like nature, is a fundamental aspect of our understanding of the universe, underpinning many technologies we rely on and revealing hidden secrets about the cosmos.
Radio Waves:
Radio waves, the longest wavelength portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, are used extensively in communication, broadcasting, and navigation. Their low energy and long wavelength allow them to penetrate atmospheric barriers and travel long distances.
- Broadcasting: AM and FM radio broadcasts utilize radio waves to transmit audio signals over vast distances.
- Communication: Cellular phones, Wi-Fi, and satellite communication all rely on radio waves to transmit information.
- Navigation: Global Positioning System (GPS) uses radio waves emitted from satellites to determine location on Earth.
- Astronomy: Radio telescopes detect radio waves from celestial objects, providing insights into the formation of stars, galaxies, and black holes.
Microwaves:
Microwaves, with wavelengths shorter than radio waves, are particularly useful for heating and communication. Their ability to excite water molecules makes them ideal for cooking and heating food in microwave ovens.
- Cooking: Microwave ovens utilize microwaves to heat food by causing water molecules to vibrate, generating heat.
- Communication: Satellite communication, radar systems, and microwave ovens all rely on microwaves for data transmission and sensing.
- Medical Imaging: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio waves and magnetic fields to produce detailed images of internal organs and tissues.
Infrared Radiation:
Infrared radiation, located between microwaves and visible light, is often referred to as "heat radiation." It plays a crucial role in thermal imaging, remote sensing, and night vision.
- Thermal Imaging: Infrared cameras detect infrared radiation emitted by objects, allowing for visualization of temperature differences. This is used in various fields, including medical diagnostics, building inspections, and security.
- Remote Sensing: Satellites utilize infrared sensors to monitor Earth’s surface, providing data on vegetation health, water distribution, and urban development.
- Night Vision: Infrared cameras and devices allow for vision in low-light conditions by detecting infrared radiation emitted by objects.
Visible Light:
Visible light, the portion of the electromagnetic spectrum that our eyes can detect, is responsible for our perception of color. It encompasses a range of wavelengths, from violet to red.
- Vision: Our eyes perceive light through photoreceptor cells in the retina, allowing us to see the world around us.
- Photography: Cameras capture light using lenses and sensors, preserving images for later viewing.
- Lighting: Artificial light sources, such as incandescent bulbs, fluorescent lamps, and LEDs, emit visible light for illumination purposes.
Ultraviolet Radiation:
Ultraviolet (UV) radiation, with wavelengths shorter than visible light, is invisible to the human eye but carries more energy. It has both beneficial and harmful effects.
- Sun Tanning: UV radiation from the sun causes tanning, but excessive exposure can lead to sunburn and skin cancer.
- Medical Applications: UV light is used in sterilizing medical equipment and treating certain skin conditions.
- Astronomy: UV telescopes study celestial objects emitting UV radiation, providing insights into the composition and evolution of stars and galaxies.
X-rays:
X-rays, with even shorter wavelengths than UV radiation, are highly energetic and can penetrate many materials. They are widely used in medical imaging and industrial applications.
- Medical Imaging: X-ray imaging allows doctors to visualize bones, teeth, and internal organs, aiding in diagnosis and treatment.
- Security: Airport security scanners utilize X-rays to detect objects concealed within luggage.
- Industrial Applications: X-rays are used in material analysis, quality control, and non-destructive testing.
Gamma Rays:
Gamma rays, the highest energy portion of the electromagnetic spectrum, are emitted from radioactive decay and nuclear reactions. They have significant applications in medicine and research.
- Cancer Treatment: Gamma rays are used in radiation therapy to target and destroy cancerous cells.
- Medical Imaging: Positron emission tomography (PET) scans use gamma rays to create images of metabolic activity in the body.
- Astronomy: Gamma-ray telescopes detect gamma rays from distant celestial objects, providing insights into the most energetic events in the universe.
FAQs about the Electromagnetic Spectrum:
Q: What are the characteristics of electromagnetic waves?
A: Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves, meaning the oscillations of the electric and magnetic fields are perpendicular to the direction of wave propagation. They travel at the speed of light in a vacuum, which is approximately 299,792,458 meters per second.
Q: How is the electromagnetic spectrum organized?
A: The electromagnetic spectrum is organized by wavelength, with longer wavelengths corresponding to lower energy and vice versa. This arrangement allows for a systematic study of the various forms of electromagnetic radiation.
Q: What are some applications of electromagnetic waves in everyday life?
A: Electromagnetic waves are ubiquitous in our daily lives. They are used in communication, broadcasting, cooking, medical imaging, security, and countless other applications.
Q: What are the potential risks associated with electromagnetic radiation?
A: While most electromagnetic radiation is harmless, high-energy radiation like X-rays and gamma rays can be harmful to living organisms. Excessive exposure can lead to radiation sickness, DNA damage, and cancer.
Tips for Understanding the Electromagnetic Spectrum:
- Visualize the spectrum: Use diagrams and illustrations to visualize the different types of electromagnetic radiation and their relative wavelengths.
- Connect applications to wavelengths: Understand how the specific wavelengths of different radiation types are utilized in various applications.
- Explore the scientific literature: Consult scientific journals and textbooks to delve deeper into the physics and applications of electromagnetic radiation.
Conclusion:
The electromagnetic spectrum is a vast and diverse landscape, encompassing a wide range of radiation that plays a crucial role in our understanding of the universe and our daily lives. From the low-energy radio waves used for communication to the highly energetic gamma rays utilized in medical treatments and astronomical research, each portion of the spectrum holds unique properties and applications. Understanding the electromagnetic spectrum is essential for comprehending the fundamental nature of light, the workings of our technological world, and the mysteries of the cosmos.





Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Electromagnetic Spectrum: A Journey Through the Waves. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply