The Cost Of Comfort: Understanding The Price Of Household Items
The Cost of Comfort: Understanding the Price of Household Items
Related Articles: The Cost of Comfort: Understanding the Price of Household Items
Introduction
With great pleasure, we will explore the intriguing topic related to The Cost of Comfort: Understanding the Price of Household Items. Let’s weave interesting information and offer fresh perspectives to the readers.
Table of Content
The Cost of Comfort: Understanding the Price of Household Items

The modern home is a complex ecosystem, filled with a vast array of items designed to enhance our lives. From the appliances that simplify daily tasks to the furniture that provides comfort and the décor that reflects our personal style, these items are woven into the fabric of our existence. However, the cost of maintaining a comfortable and functional home has become a significant financial consideration in today’s economic climate. This article delves into the factors influencing the price of household items, exploring their impact on household budgets and offering insights into how consumers can navigate this landscape effectively.
Factors Influencing Household Item Prices:
The price of household items is a complex interplay of several factors, including:
1. Raw Materials and Manufacturing Costs: The cost of materials used in manufacturing household items plays a crucial role in determining their final price. Fluctuations in the global commodity market, driven by factors like supply and demand, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions, can significantly impact the price of raw materials such as steel, aluminum, wood, and plastics. For example, the price of lumber skyrocketed during the COVID-19 pandemic due to supply chain disruptions and increased demand for home improvement projects, leading to a corresponding increase in the cost of furniture and other wood-based products.
2. Labor Costs: The cost of labor involved in the production, transportation, and retail of household items is another significant factor. Wages, benefits, and labor regulations all contribute to the overall cost. In regions with higher labor costs, the price of manufactured goods tends to be higher. Additionally, labor shortages, particularly in skilled trades, can lead to increased costs as companies compete for limited talent.
3. Technology and Innovation: Technological advancements in manufacturing processes and product design can drive both cost reductions and price increases. While automation can lead to lower production costs, the development of new materials and features often comes with a premium price tag. For example, the introduction of energy-efficient appliances may initially be more expensive but can lead to long-term savings on utility bills.
4. Brand Recognition and Marketing: Brand recognition and marketing campaigns play a significant role in shaping consumer perceptions and influencing purchasing decisions. Well-established brands often command higher prices due to their reputation for quality, reliability, and brand image. Marketing expenses, including advertising, promotions, and distribution, are ultimately reflected in the final price of the product.
5. Shipping and Transportation Costs: The cost of transporting goods from manufacturing facilities to retail locations adds to the overall price. Rising fuel costs, tariffs, and trade regulations can significantly impact shipping expenses. Consumers often bear the brunt of these costs, particularly for items purchased online or shipped from overseas.
6. Retail Markups and Competition: Retailers add their own markups to the cost of goods to ensure profitability. The level of competition in the market can influence retail markups. In highly competitive markets, retailers may offer lower markups to attract customers, while in markets with fewer competitors, markups may be higher.
7. Demand and Supply: The basic principles of supply and demand also apply to household items. When demand for a particular item exceeds supply, prices tend to rise. Conversely, when supply exceeds demand, prices may fall. Seasonal fluctuations, trends, and consumer preferences can all influence demand and impact pricing.
8. Government Regulations and Taxes: Government regulations, including safety standards, environmental regulations, and taxes, can impact the cost of manufacturing and selling household items. For example, tariffs on imported goods can increase the price of certain items.
Understanding the Cost of Comfort: Implications for Consumers
The cost of household items is a significant factor in household budgets, particularly for low- and middle-income families. Rising prices can strain household finances, leading to difficult choices about spending priorities. Consumers can navigate this landscape by adopting the following strategies:
1. Prioritize Needs Over Wants: It’s essential to differentiate between essential household items, such as appliances and furniture, and non-essential items, such as decorative items and gadgets. Focusing on purchasing items that meet basic needs can help stretch household budgets further.
2. Shop Around and Compare Prices: Comparing prices from different retailers, both online and offline, can help identify the best deals. Utilize price comparison websites and apps to streamline the process.
3. Consider Used or Refurbished Items: Purchasing used or refurbished items can significantly reduce the cost of household items, especially for durable goods like furniture and appliances. Reputable online marketplaces and local consignment shops offer a wide selection of pre-owned items at reduced prices.
4. Opt for Generic Brands: Generic brands often offer similar quality at lower prices compared to name-brand products. This is particularly true for items like cleaning supplies, toiletries, and food.
5. Take Advantage of Sales and Promotions: Retailers often offer sales and promotions, especially during holiday periods and seasonal changes. Be on the lookout for discounts, coupons, and loyalty programs to save money.
6. Consider DIY Projects: For simple repairs and upgrades, consider undertaking DIY projects to reduce the cost of hiring professionals. Online resources and tutorials offer a wealth of information and guidance for DIY enthusiasts.
7. Invest in Durable Goods: Choosing durable, high-quality items can reduce the need for frequent replacements, ultimately saving money in the long run. While these items may have a higher upfront cost, they can provide lasting value and reduce overall expenses.
8. Embrace Minimalism: Adopting a minimalist lifestyle can help reduce the number of items purchased, leading to significant savings. Consider decluttering your home regularly and only purchasing items that truly serve a purpose.
FAQs: Understanding the Cost of Household Items
Q: Are household item prices rising faster than inflation?
A: While overall inflation has been rising in recent years, the price of certain household items, such as furniture, appliances, and building materials, has increased at a faster rate due to supply chain disruptions, labor shortages, and increased demand.
Q: How can I find the best deals on household items?
A: Utilize price comparison websites and apps, shop during sales and promotions, consider used or refurbished items, and explore online marketplaces and local consignment shops.
Q: What are some tips for budgeting for household items?
A: Prioritize needs over wants, create a budget for household expenses, shop around and compare prices, take advantage of sales and promotions, and consider DIY projects.
Q: How can I reduce my spending on household items?
A: Embrace minimalism, declutter your home regularly, avoid impulse purchases, and prioritize essential items over non-essential ones.
Tips for Managing the Cost of Household Items:
1. Create a Budget: Allocate a specific amount for household expenses, including furniture, appliances, and other items. This will help you stay within your budget and avoid overspending.
2. Track Your Spending: Monitor your spending on household items to identify areas where you can cut back. Use budgeting apps or spreadsheets to track your expenses.
3. Set Realistic Expectations: Understand that the cost of household items can fluctuate, and it’s important to set realistic expectations for your budget.
4. Consider Long-Term Savings: When purchasing durable goods, think about the long-term cost savings they may offer. Investing in high-quality items can reduce the need for frequent replacements.
5. Take Advantage of Resources: Utilize online resources, consumer reports, and product reviews to make informed decisions about purchasing household items.
Conclusion:
Navigating the cost of household items in today’s economic climate requires careful planning and strategic decision-making. Understanding the factors influencing prices, adopting smart shopping strategies, and embracing a mindful approach to consumption can help consumers manage their household expenses effectively. By prioritizing needs, comparing prices, considering alternative options, and investing in durable goods, consumers can create a comfortable and functional home without breaking the bank.



:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/factors-affecting-real-estate-market.asp_final-8e8ea4cd40dd45909593384700de9759.png)



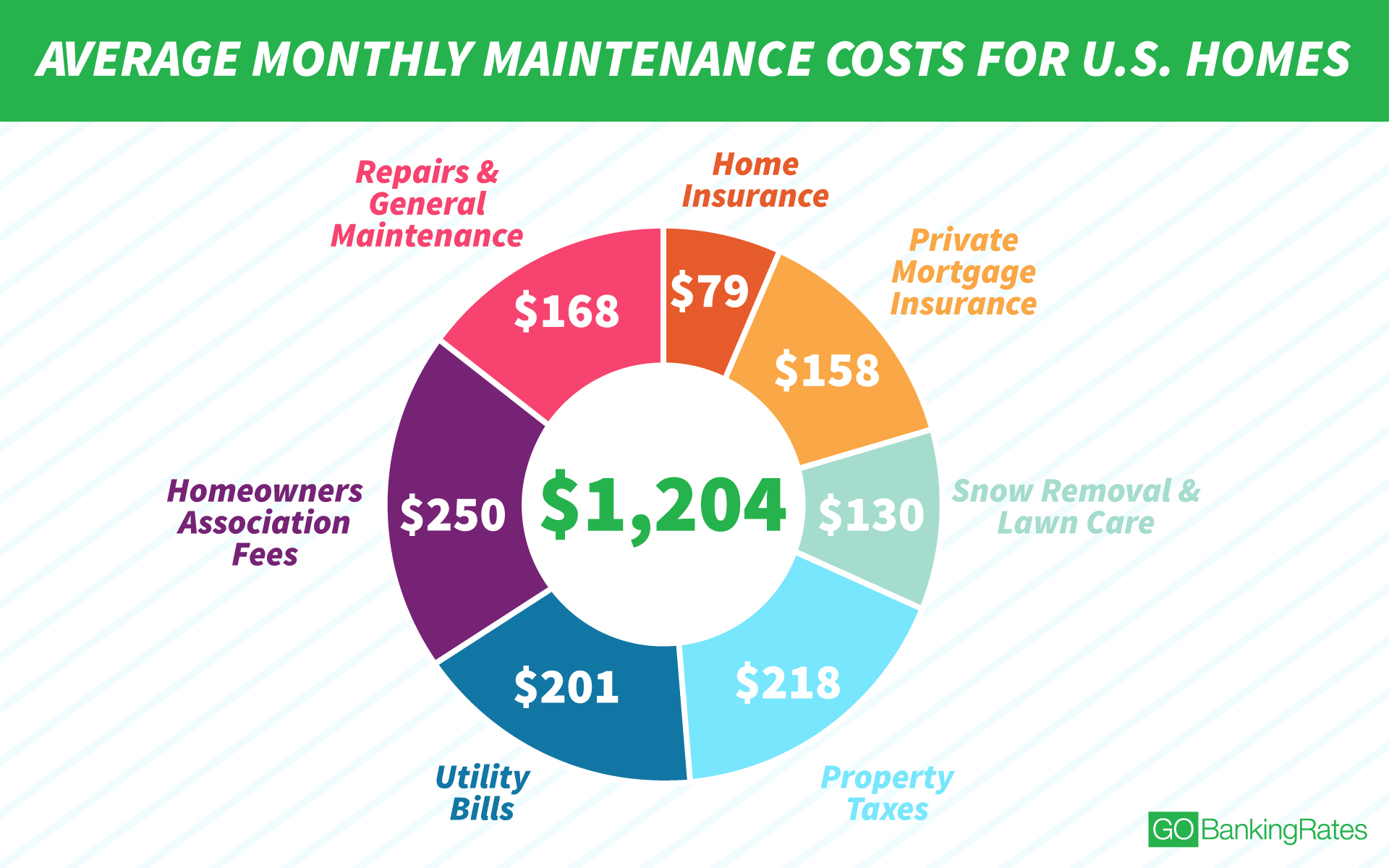
Closure
Thus, we hope this article has provided valuable insights into The Cost of Comfort: Understanding the Price of Household Items. We thank you for taking the time to read this article. See you in our next article!
You may also like
Recent Posts
- The Ubiquitous "T": A Journey Through Objects And Concepts
- Navigating The World Of Household Waste Removal: A Comprehensive Guide
- Navigating The Aftermath: A Comprehensive Guide To Post-Mortem Planning
- The Science Of Slime: A Guide To Creating Viscous Fun From Common Household Ingredients
- A Culinary Journey: Exploring Kitchen Household Items And Their Significance
- Navigating The Local Market: A Guide To Selling Household Items
- The Essentials Of Human Existence: A Comprehensive Look At The Items We Need
- The Intriguing World Of Six-Inch Objects: Exploring Everyday Items With A Specific Dimension
Leave a Reply